What is Control Survey?
Additionally, Control Survey provide “basic control” or Parallel and Upright positions of points. Similarly, this survey is Necessities for some other Supplemental surveys.
Specifically, Survey Control Points Sometimes we termed as Geodesic surveys as well. Additionally, we conduct this survey to provide Geographical positions and plane Positions of Trilateration. Likewise, we also apply a control survey for Passage stations and the Altitudes of Standards. Furthermore, these control points usable as Citations for Bathymetric surveys. But also, For topographic control and to control many states, city surveys- we can use previous Control surveys.
Moreover, We can collect Control Survey data from any registered Topographer and also available from a government authority.

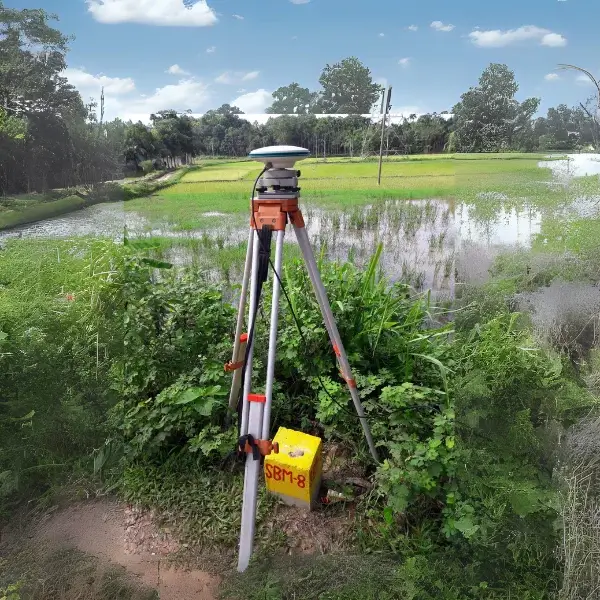
Control Survey
Control Survey is a surveying process that determines accurate coordinates, elevations, and latitude-longitude information. This survey is typically used for land surveying, construction projects, and geographic data collection. The main objectives of a Control Survey are:
1. Determining Accurate Coordinates: It creates precise coordinates at various locations, which serve as a foundation for subsequent surveys and construction.
2. Modeling and Mapping: It serves as a basis for local and national mapping systems, enabling future surveys and planning.
3. Ensuring Construction Accuracy: Control surveys are used to verify accurate coordinates and elevations in construction projects.
4. Measuring Distances and Angles: It helps determine essential measurements, such as distances and angles.
Generally, Control Surveys can be of two types: Horizontal Control Survey and Vertical Control Survey, which respectively measure distances and elevations between local points.
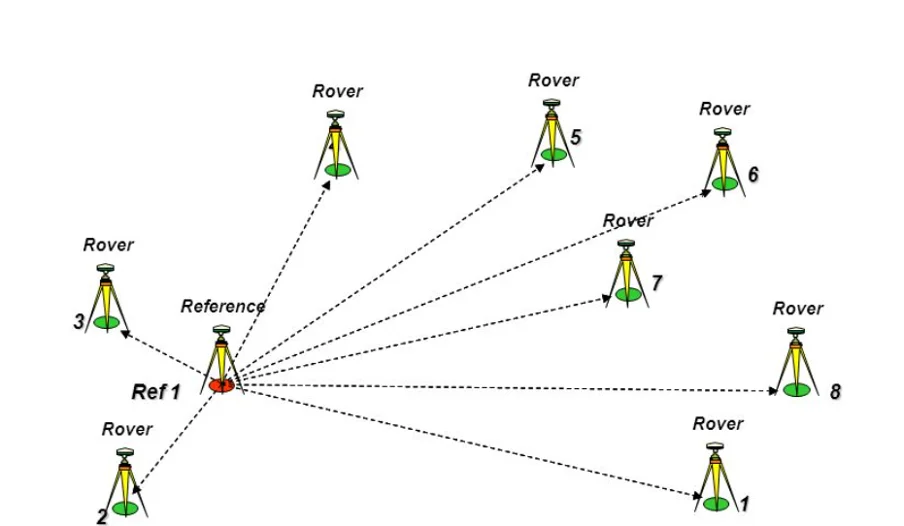
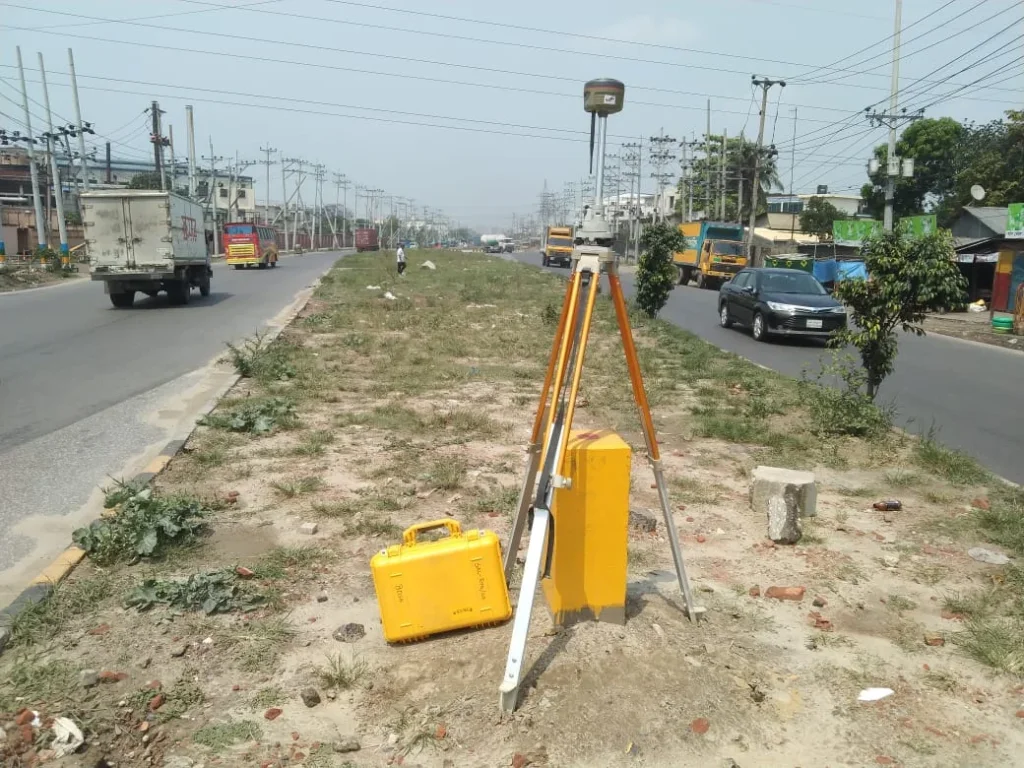
Control Survey with RTK GPS
Using RTK GPS (Real-Time Kinematic Global Positioning System) for control surveys offers several advantages, including:
- High Accuracy: RTK GPS can achieve high precision, typically within 2 centimeters. This level of accuracy is particularly important for construction and land surveying.
- Rapid Data Collection: RTK technology provides real-time data, which accelerates the surveying process. This results in time savings and allows for efficient completion of tasks.
- Ease of Use: The RTK GPS system is generally user-friendly and provides effective guidance for operators, reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Compact and Portable: RTK GPS devices are usually lightweight and compact, making them easy to carry. This convenience is beneficial for surveying in various locations.
- Multi-Purpose Use: In addition to control surveys, RTK GPS can be employed in agriculture, transportation, construction, and other fields.
- Land Feature Analysis: RTK GPS enables accurate analysis of land features such as boundaries, elevations, and geographical locations.
- Dispute Resolution: It provides accurate and reliable information to resolve land-related disputes, supporting claims of ownership.
- Informed Project Planning: Enhanced data facilitates easier planning for future projects and helps establish a solid foundation for various tasks.
Using RTK GPS for control surveys makes operations more effective, faster, and reliable, which is crucial for the success of various projects.
Control Points using GNSS GPS
The primary purpose of establishing control points using GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) and GPS (Global Positioning System) is to provide precise positional and elevation data for land surveying, construction, and other projects. When control points are set up using GNSS GPS, they create a foundation of accuracy and stability for subsequent surveys and projects.
Some advantages of establishing control points using GNSS GPS are as follows:
- High Accuracy: GNSS GPS technology can achieve a precision of up to 1-2 centimeters, making it ideal for establishing control points.
- Large Area Coverage: GNSS GPS systems allow for easy establishment of control points over large areas. By receiving satellite signals from various positions, this technology can cover extensive and remote regions.
- Fast Point Establishment: Using GNSS GPS, control points can be quickly set up as it directly receives data from satellites and provides real-time information.
- Ease of Use: GNSS GPS systems are generally easy to operate, requiring minimal training for operators to begin working.
- Permanent Control Points: Control points established with GNSS GPS are reliable for long-term projects. These points can be reused in future projects, ensuring consistency and accuracy in measurements.
- Multi-purpose Control: Control points established using GNSS GPS are not only useful for surveys but also for transportation, road construction, hydroelectric projects, and urban planning.
Steps for Setting Up GNSS GPS Control Points:
- Site Selection: First, a stable and open site is selected where satellite signals can be easily received.
- Data Collection: GNSS GPS devices are used to collect positional and elevation data, which helps in precisely establishing control points.
- Data Processing: The collected data is analyzed and stored for future use.
- Marking: After setting up the control point, it is physically marked so that it can be easily identified in the future.
Establishing control points using GNSS GPS makes project execution more accurate, faster, and reliable, leading to successful project outcomes.
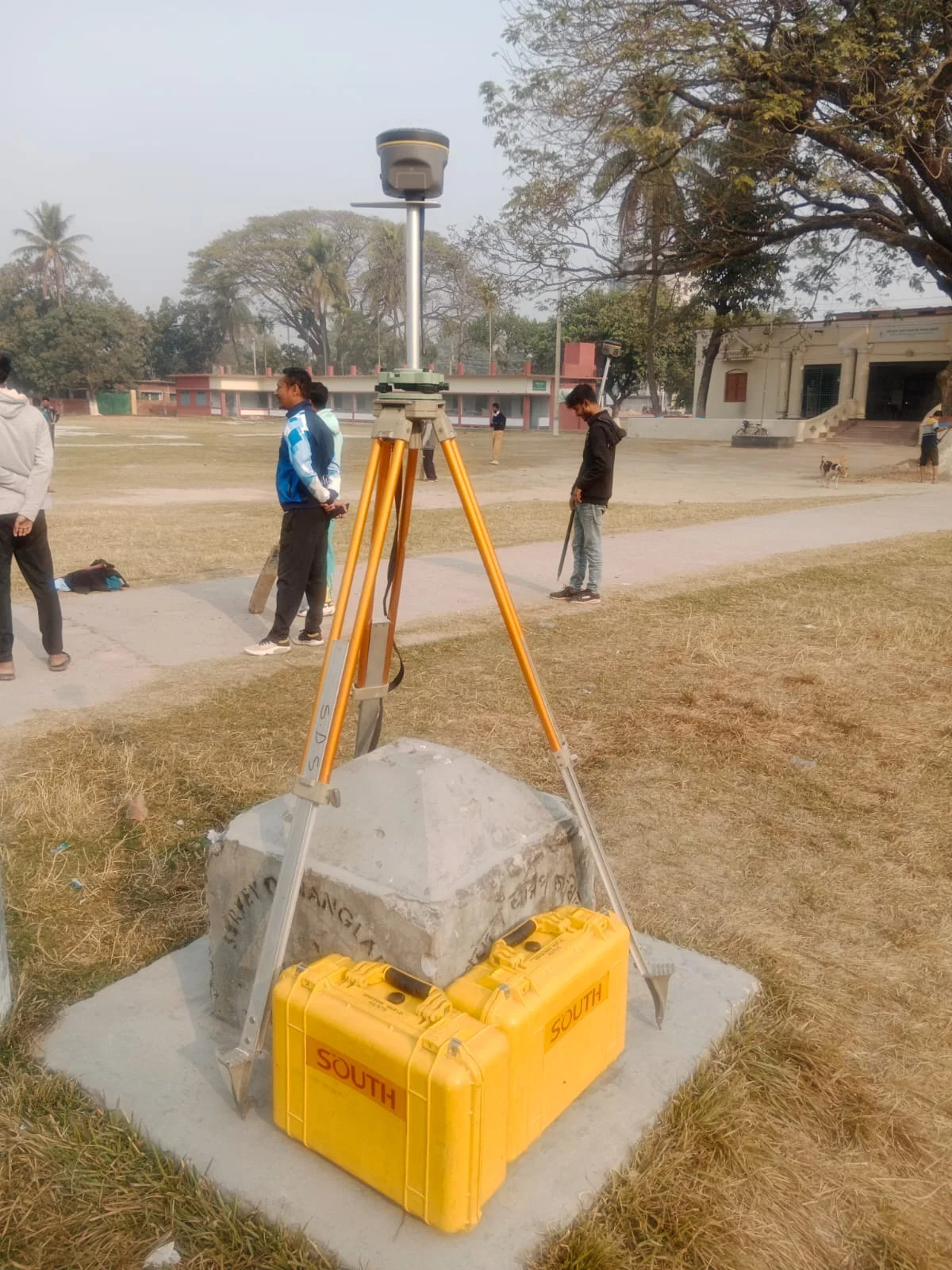

Using RTK and Static Control Survey
Both RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) survey and static control survey use GPS/GNSS technology to determine precise coordinates for land and other locations. However, there are differences in their purpose, process, and usage.
1. Using RTK (Real-Time Kinematic)
RTK survey is a real-time method that ensures accuracy and speed by using a base station and a rover station. It is popular for the following advantages:
Advantages:
- Real-time data: In RTK, the base station communicates real-time data with the rover station, providing precise coordinates instantly.
- High accuracy: RTK technology offers accuracy up to 1-2 centimeters, making it highly effective for agriculture, construction, and other projects.
- Fast data collection: RTK can collect data quickly, saving time when surveying large areas.
- Ease of use: RTK systems are typically easy to use, allowing operators to work with minimal training.
Limitations:
- Range limitation: The rover station must typically be within 10-20 kilometers of the base station, limiting its use in larger projects.
- Line of sight: A clear line of sight is required between the base and rover stations. Obstacles like trees, large buildings, or hilly terrain can interfere.
2. Static Control Survey
Static surveying is a control survey method where a GPS receiver remains stationary at multiple points for extended periods to collect data. This method is used for survey projects that require high accuracy.
Advantages:
- Extremely high accuracy: Static surveys can provide accuracy up to 3-5 millimeters, essential for precise control point establishment.
- Large area coverage: This method is effective for collecting data over large areas without requiring real-time connections.
- Ability to capture satellite signals: Static surveying collects satellite signals for a long time, reducing the impact of environmental obstacles like trees or buildings.
Limitations:
- Time for data processing: Static surveying is not real-time, so processing data after collection takes time.
- Slower than RTK: Compared to RTK, static surveys are slower, as data must be collected at each point over a long period.
Comparison Between RTK and Static Surveys:
| Feature | RTK Survey | Static Control Survey |
| Data collection method | Real-time data | Long-duration data collection |
| Accuracy | 1-2 centimeters | 3-5 millimeters |
| Speed | Fast data collection | Slower, as data is collected for a long time at each point |
| Range | Limited to 10-20 km from the base station | Can cover large areas |
| Usage | Used for general surveys and construction projects | Used for projects requiring high accuracy |
Conclusion:
RTK GPS is ideal for quick and efficient data collection, especially when both accuracy and speed are required. On the other hand, static control surveys are suited for projects requiring high precision, where data is collected over a large area for longer periods to determine exact coordinates and elevation.
Processes of Control Surveying
The Procedures in carrying out the survey as follows:
The Control Survey Process is an important procedure for determining accurate coordinates and elevation data for land, construction, and other projects. It is completed in several stages, ensuring high precision and reliability. The control survey process generally follows these steps:
1. Initial Planning and Preparation:
- Define the Purpose: First, determine the type of control survey needed based on the project’s objectives.
- Site Inspection: Conduct a site visit to ensure the correct location for the survey. The site’s environment, terrain, and satellite signal accessibility are evaluated.
- Equipment Preparation: Ensure the necessary equipment such as GNSS receivers, RTK systems, static receivers, theodolites, etc., are properly prepared.
2. Control Point Location Selection:
- Ensure Stability: Select a site that is stable and suitable for long-term data storage.
- Satellite Signal Accessibility: Choose a location that offers clear skies and good satellite signal reception to collect accurate data from satellites.
3. Data Collection:
- Using GNSS/RTK: Data is collected at control points using GNSS or RTK technology, which can be done in real-time or using static methods.
- Collecting Multiple Points: In many cases, data is collected from multiple points to ensure accuracy.
- Long Duration Data Collection: For high precision, especially in static methods, data is collected at specific points over extended periods.
4. Data Processing and Analysis:
- Using Data Processing Software: Collected data is input into processing software to identify and correct any errors and to determine accurate coordinates and elevations.
- Correction and Validation: After analyzing the data, corrections are made, and the accuracy is validated.
5. Presentation of Results:
- Providing Accurate Coordinates and Elevations: Final data is processed to deliver precise coordinates, elevations, and other important information.
- Mapping and Modeling: Based on the data, maps are created and models are developed for future planning.
6. Data Storage and Reporting:
- Preparing Reports: A report is generated with all the data and analysis for future reference.
- Data Storage: The necessary data is securely stored so it can be reused if the same site is revisited for future work.
7. Identification and Reuse:
- Marking Control Points: Each control point is physically marked so that it can be easily identified in the future.
- Reuse: As required, the same control points can be used in future projects.
Conclusion:
When executed correctly, the control survey process ensures stability, precision, and efficiency in land management, construction projects, and other related undertakings.
Examples of CONTROL SURVEY
Similarly, The Primary Control surveying shall consist of a closed-loop network. Likewise Subsequently, should have adequate redundancy, precision and accuracy. Moreover, Survey records shall include documentation of Primary Control. Specifically, The work shall include the correct location of the monuments. Therefore, installing the monuments, and verifying the positional accuracy of the monument. Likewise, A Primary Control survey should meet the horizontal and vertical accuracy with tolerances level.

