What is meant by leveling?
The process or technique through which the relative height or depth of various objects or points on the earth’s surface is determined is called leveling.
What is meant by elevation and comparative elevation?
Answer: The height of any point on the earth’s surface from a specific datum plane or line is referred to as the elevation of that point. On the other hand, the difference in elevation between any two points is called the comparative elevation (height or depth) of those two points.
Why is leveling done, or what is its purpose or necessity?
Answer: Leveling is done for the following reasons:
(1) To determine the alignment and cross-sectional profile or undulation of the ground along various route projects such as roads, railways, irrigation canals, and water or sewer lines during site selection.
(2) To ascertain the quantity of earth to be excavated or filled for roads, railways, irrigation canals, etc.
(3) For drainage projects, to select the locations of ridge or valley lines and to design the dimensions of the sewer for proper drainage and to determine the area of the drainage region.
(4) To determine the topography of the proposed reserved land for buildings.
(5) To determine the volume of any water body or catchment area from contour maps.
(6) To install additional benchmarks for local leveling work.
(7) To establish or verify the formation level of roads, railways, etc.
(8) To level the ground of a specific area to a designated height.
(9) To determine the slope of roads, railways, canals, roofs, floors, etc.
(10) To ascertain the highest flood level (H.F.L.) during the construction of bridges, culverts, roads, railways, and buildings.
(11) To check the levelness of the foundation during the construction of structures.
(12) Leveling is also done for various tasks, including preparing contour maps.
What is meant by sounding reduction?
The water surface of tidal flows or flowing water bodies is not always stationary; instead, it fluctuates. As a result, it is not possible to take soundings from the same water level at different points. To address this, a gauge reading is taken each time soundings are measured at various points. The process of determining the value of sounding at each point by applying gauge corrections with the help of the gauge readings and the soundings concerning a specific datum is known as sounding reduction.
What is meant by fly leveling?
Fly leveling refers to the leveling work done by taking only forward and backward readings to carry the elevation from a benchmark to a distant location or to determine the elevation of a specific place.

What is meant by a benchmark?
A benchmark is a specific reference point whose elevation or reduced level (RL) is known. These are established at important locations.
Purpose:
- To determine the elevation or relative height or depth of various points at specific distances along a designated alignment.
- To serve as a reference for future survey work.
- To change the direction of a specific level line.
- To initiate leveling at the start of daily work or to continue ongoing tasks.
- To verify the accuracy of leveling work, etc., benchmarks (BMs) are used.
Types:
Benchmarks are mainly classified into four types: - GTS (Geodetic Survey) Benchmarks.
- Permanent Benchmarks.
- Established Benchmarks.
- Temporary Benchmarks.
(a) G.T.S Benchmarks (Great Triangulation Survey):
The National Survey Organization conducts a highly precise triangulation survey and establishes G.T.S benchmarks at various distant locations throughout the country. The location and elevation of these benchmarks are published in a list by the organization.
(b) Permanent Benchmarks (P.B.M.):
These are important and permanent reference points among G.T.S benchmarks. They are clearly marked and established by government organizations such as P.W.D., R&H, and WAPDA on structures like bridge or culvert parapet walls, building corners, gate pillars, mile or kilometer markers, etc.
(c) Arbitrary Benchmarks (A.B.M.):
In minor leveling tasks where the relative elevation changes of various points need to be determined and are not related to M.S.L (Mean Sea Level), any benchmark assigned at a convenient location or point, such as a building plinth, is referred to as an arbitrary benchmark.
(d) Temporary Benchmarks (T.B.M.):
At the end of a workday or during breaks, temporary benchmarks are established for use as reference points for resuming work the following day. These benchmarks are carefully placed at relatively permanent objects, such as a culvert, the base of a large tree, gate pillars, or stakes in firm soil.
Mean Sea Level (M.S.L.):
The mean sea level is determined by calculating the average height of the sea’s tidal surface over a period of 30 to 35 years. The average is taken from an equal number of gauge readings for high and low water spring tides (H.W.O.S. and L.W.O.S.) over a lunar month. In this way, the average height of the sea surface (M.S.L.) is determined by taking readings at various times throughout the year and over multiple years, and the elevation is established on the benchmarks at the seashore. The R.L (Reduced Level) of M.S.L. is considered zero. If a point’s elevation is above or below this level, its R.L. is regarded as positive or negative, respectively.
What is meant by Datum of Reduction (DR)?
Datum of Reduction is abbreviated as DR. The average height of the sea’s tide over 30 to 35 years is considered the mean sea level. This level is referred to as the datum. At the seashore, it is recorded as 0.000M in the form of a benchmark (BM). The R.L. (Reduced Level) for survey data areas is determined from this datum. This R.L. or base level is referred to as the Datum of Reduction.

Why is Fly Leveling Done?
Fly leveling is done to carry the elevation from a benchmark to a distant point. Fly leveling is a surveying method primarily used to determine the heights of elevated and lower areas. It is extremely important for geotechnical, construction, and other infrastructural activities. Here are some main reasons for performing fly leveling:
Reasons for Fly Leveling:
- Height Determination: It helps in determining the height of specific locations within a project, which is especially essential in construction and design processes.
- Land Position Analysis: It assists in analyzing the land’s structure and geological positioning, providing important information for project planning and design.
- Hydraulic Projects: It helps in determining the correct height for reservoirs, rivers, or pipelines, which is important for managing and controlling water flow.
- Soil Testing: It aids in verifying the suitability of the soil at necessary locations for construction. Fly leveling assists in determining the correct height during soil testing.
- Construction Planning: It helps in creating accurate plans for constructing buildings, bridges, or any other infrastructure. Determining heights enhances accuracy during the construction process.
- Drainage System Design: It aids in creating proper drainage systems, ensuring that water flows out correctly and preventing waterlogging.
- Infrastructure Stability: It helps ensure the stability of constructed infrastructure. Confirming correct heights guarantees the permanence of buildings or bridges.
- Improvement of Internal Environment: It ensures correct heights and leveling for the internal environment, helping to regulate climate and ensure proper ventilation.
Fly leveling is a highly important process that provides accurate height and level information, which is essential for the success of subsequent projects.
What is a Horizontal Control?
Horizontal control refers to the reference points established at the beginning of hydrographic survey work for measuring or testing horizontal distances.
What is a Vertical Control?
Vertical control refers to the determination of the vertical height of other points from a benchmark located near riverbanks or seashores.
Objectives of Leveling:
The objectives of leveling are as follows: - To determine the relative height or depth of various points or objects.
- To measure the quantity of earth cut and filled for roads, highways, irrigation, and canals.
- To create contour designs, determine soil quantities, and assess the capacity of water bodies.
- To establish permanent benchmarks in an area.
- To determine the formation level of roads or railways.
- To identify the highest flood level.
- To use leveling in the context of building plinth levels, floors, roofs, etc.

What are Surveying and Leveling?
Surveying and leveling refer to the processes or techniques by which the relative elevations or depths of various points or objects on the Earth’s surface are determined. Surveying is the precise measurement, mapping, and analysis of land or terrain. This process determines the shape, size, and characteristics of land. Through surveying, the accurate position and measurement of various land features like roads, buildings, rivers, and other elements can be established. It is generally conducted using tools such as theodolites, GPS, leveling instruments, and chains.
Purpose of Surveying and Leveling
(a) To implement various route projects like roads, railways, irrigation canals, water, or drainage lines by determining the alignment of their surfaces and the profile or gradient of the horizontal surface.
(b) To determine the quantity of soil to be cut or filled in various projects.
(c) To define drainage areas and design suitable drainage systems during drainage projects.
(d) To conduct topographical assessments of proposed reserved areas for construction.
(e) To calculate the volume of any reservoir or water body area from a contour map.
(f) To install additional benchmarks (BMs) at lower elevations as required.
(g) To inspect the prepared surface of roads, railways, etc.
(h) To survey and level land in a specific area to a specified elevation.
(i) To determine slopes for roads, railways, canals, roofs, floors, etc.
(j) To establish maximum floodplains during the construction of bridges, culverts, roads, railways, and buildings.
(k) To monitor foundation level leveling during environmental installations.
What Equipment Do We Use for Surveying and Leveling Work?
Similarly, for determining the elevation of various points, we primarily use four items in leveling work, which are:
(a) Surveying and leveling instrument
(b) Staff
(c) Chain or tape
(d) A leveling field book or logbook
With the help of a leveling instrument, we can obtain a horizontal line of sight at any point on the Earth’s surface. Likewise, a horizontal line of sight allows us to measure the vertical distance to a point using the staff, while the chain or tape is used to measure distances between various points. Additionally, we record the readings from the staff, along with all other field details, in the field book.
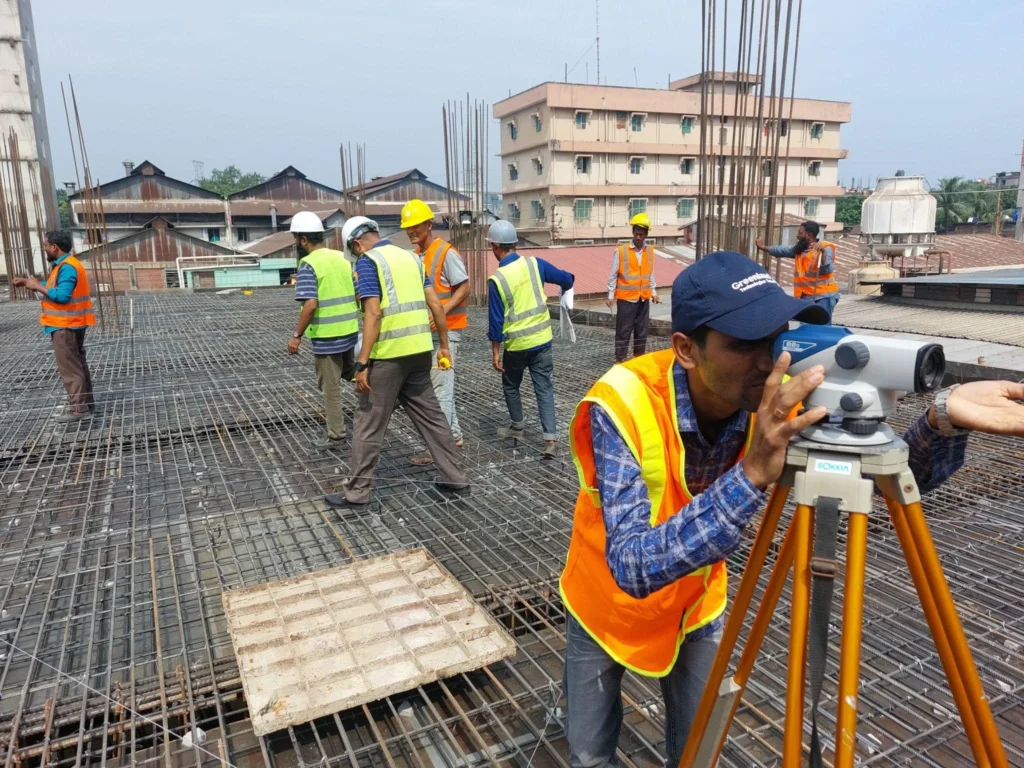

The Importance of Surveying and Leveling in Fieldwork
Surveying and leveling are highly significant in fieldwork as they provide accurate measurements and help understand the topography and layout of a specific area. Here are some of the main points that highlight their importance:
1. Accurate Planning and Design: Surveying and leveling are essential for the design and planning of roads, railways, canals, and drainage systems. They ensure that the project is properly aligned with the area’s topography.
2. Foundation and Structural Stability: Proper leveling is critical for laying the foundation of buildings. It ensures that buildings, bridges, and other structures are level and secure.
3. Land Assessment and Valuation: Surveying and leveling provide data on the elevation, slope, and other underground characteristics of the land, which help evaluate the suitability of land use for various projects.
4. Volume Estimation: Surveying and leveling aid in determining the amount of material required for excavation and fill work, which ensures accurate budgeting and resource allocation.
5. Drainage and Water Flow Management: Surveying helps in determining slopes and gradients, which is essential for designing proper drainage systems, ensuring water flow, and preventing flooding and erosion.
6. Topographic Mapping: Surveying and leveling facilitate the creation of topographic maps, which are useful for land and environmental studies.
7. Enhanced Safety and Precision: By providing accurate data, surveying and leveling help reduce risks and ensure safety in projects.
In summary, surveying and leveling play an essential role in fieldwork, as they ensure accurate planning, reliability, and safety in various projects.
Differential Surveying and Leveling
Moreover, differential surveying and leveling involve measuring the vertical distance from a known elevation point to determine the elevation of unknown points. The most common methods for determining elevation include:
- A compensator-type, automatic (engineering level) instrument and leveling rod(s)
- An electronic digital bar-coded leveling instrument with a bar-coded rod
Similarly, thorough knowledge of leveling principles and the correct application of methods and tools will help prevent costly delays while ensuring the desired accuracy and results.
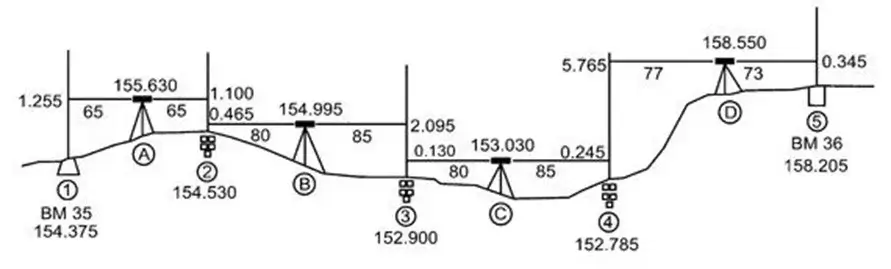
Preferred Methods for Obtaining Elevation (Ranked by Preference/Accuracy)
Different methods are used for determining elevation, ranked below in order of accuracy and preference:
1. Precision Leveling: This method provides the highest accuracy and is typically used in engineering and construction projects where maximum precision is required.
2. Differential Leveling: This method involves measuring from a known elevation point to an unknown point. It is very accurate and widely popular in engineering and surveying work.
3. Trigonometric Leveling: Elevation is determined using angle and distance measurements. It is applicable for long distances and offers accuracy close to that of precision leveling.
4. Barometric Leveling: Elevation is determined based on air pressure. It is comparatively less accurate and generally used for research or large geographical area assessments.
5. GPS Leveling: This method determines elevation based on satellite data. It is easy and quick but may be less accurate than precision leveling.
The choice among these methods depends on the requirements and the desired level of accuracy.
Equipment at an Unknown Elevation Point
Similarly, with a comprehensive understanding, we provide leveling services to our clients. Specifically, due to the knowledge and expertise of our team, we have been able to meet our clients’ needs. Likewise, we have intelligent employees who agree with defined instructions while offering these services.
Service Description
- Additionally, Sonar Bangla Survey Consultants is well-equipped and prepared to offer an excellent range of surveying and leveling services.
- Furthermore, the goal of leveling is to determine the relative heights of various objects above or below the Earth’s surface and to ascertain the undulations of the ground surface.
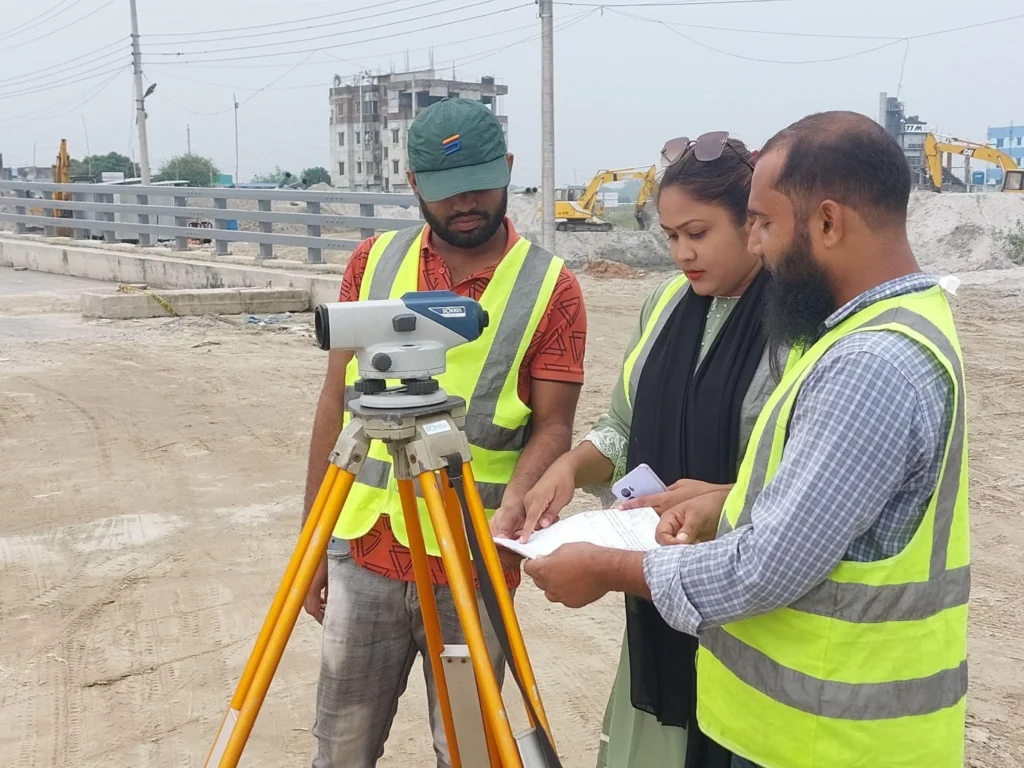

Land Survey and Leveling Services
Moreover, with our vast experience and knowledge in this field, we offer the best quality array of land survey and leveling services to our esteemed clients. Furthermore, we are highly respected in the industry for adhering to the latest technical standards while conducting our services. In particular, we aim to carefully consider all aspects of the underlying circumstances before reaching the final report.
Conclusion
As you stand atop a hill, gazing out at the undulating landscape, you’re reminded of the ancient Greek myth of Daedalus, who mastered the art of traversing complex labyrinths.
Similarly, a contour survey is your map, guiding you through the twists and turns of the terrain.
With its precise measurements and intricate lines, it’s your key to deciphering the secrets of the land, ensuring your construction projects are built on solid ground.
For a professional and accurate contour survey, call Sonar Bangla Survey Consultants office at +880 1742 585592 to get a free quotation from a team with a proven track record of excellence, boasting over 150 5-star reviews on Google.

