Definition of Project Surveying
Project surveying refers to all types of fieldwork related to the planning and construction of engineering projects such as railways, highways, irrigation canals, sewer lines, tunnels, and dams, along with the necessary calculations, maps, profiles, and related designs.
The planning and construction methods of a project must be designed to ensure economic viability and maximum utilisation. Each project has its own unique characteristics and peculiar challenges that require economically viable solutions, taking various factors into account. The success of a project largely depends on the comprehensive knowledge and sound judgement of the project engineer, which in turn relies on the timely execution of tasks and the availability of necessary funds.
List of Instruments Required for Project Surveying
The following is a list of instruments commonly used in project surveying: (i) Transit Theodolite
(ii) Levelling Instrument (for levelling)
(iii) Sextant
(iv) Telescope or Binoculars
(v) Plane Table
(vi) Engineering Chain
(vii) Surveyor’s Compass
(viii) Subtense Bar
(ix) Levelling Staff
(x) Prismatic Compass
(xi) Tape Measure
(xii) Clinometer
(xiii) Optical Square
(xiv) Barometer
Accessories:
(1) Mouza Map of the Area
(2) Necessary stakes, spades, ropes, lime, hammers, etc.
Names of Different Engineering Projects:
Engineering projects are undertaken based on the type of work and necessity. Below are some examples of engineering projects:
(i) Highway Project
(ii) Railway Project
(iii) Airport Project
(iv) Waterway Project
(v) Sewer and Pipeline Project
(vi) Irrigation Canal Project
(vii) Tunnel Project
(viii) Dam and Reservoir Project
(ix) Hydrographic Project
(x) Power Generation Project
(xi) Bridge and Culvert Project
(xii) Building Construction Project
(xiii) River Training Project
(xiv) Mining Project
(xv) Maintenance Project, etc.
(Mention the Step of Project Surveying)
(i) Reconnaissance survey
(ii) Preliminary survey
(iii) Final Location survey
(iv) Construction survey

What are the Advantages of Digital Surveying?
Digital surveying refers to the land surveying conducted using digital methods or instruments. Officials state that digital surveying allows for easy measurement of land while ensuring transparency in land ownership and dimensions. The first land survey in this region began in 1888 in Ramu, Cox’s Bazar district.
Digital land surveying helps you understand the boundaries of your land. A survey is conducted to identify, describe, monument, and map the boundaries and angles of a land parcel. This may include the parcel’s topography, the locations of buildings, and other improvements made to the parcel. The main surveying instruments used worldwide include the theodolite, measuring tape, total station, 3D scanners, GPS/GNSS, levels, and rods. Most instruments are secured on a tripod for use. Measuring tape is commonly used for measuring short distances.
The theodolite is an instrument used for measuring angles. It measures angles in both the horizontal and vertical planes using two separate circles, protractors, or aligned systems.
A simple method for measuring elevation is using an altimeter, which finds altitude based on air pressure. When more precise measurements are required, surveys are conducted using a digital total station or digital theodolite to ensure the accuracy of the land’s boundaries. Distances and coordinates can be measured with the help of a total station.
Additionally, to conduct accurate digital land surveys, Bangladesh is reported to be utilising technologies such as Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), fourth-generation survey drones or UAVs, ground control stations, Global Positioning System (GPS), electronic total stations (ETS), data recorders, and plotters.
The Survey Department states that once the digital survey is completed, there will be no need for repeated surveys in the field, except in the case of major land discrepancies caused by natural factors. The land survey department hopes that this will lead to a radical change in land management, a reduction in court cases, an increase in government revenue, and an improvement in law-and-order situations.
New mouza designs can be prepared in digital surveys, which is known as traverse surveying. The location of the mouza will be identified through satellite imagery. Following this, the mouza map or design will be drawn digitally, referred to as “Kashaya.”

Use of Total Station
A Total Station is a versatile and essential surveying instrument that combines the functions of an electronic theodolite and an electronic distance measurement (EDM) device. It plays a significant role in various fields, including construction, engineering, and land management. Here are some of its primary applications:
- Topographic Surveys: Total Stations are widely used to create detailed topographic maps by measuring elevations and land slopes. This data is critical for planning and design purposes in engineering projects.
- Construction Projects: They facilitate the precise determination of locations and angles during construction, ensuring that structures are built according to specifications. This helps in minimising errors and reducing rework.
- Architectural Design: Architects use Total Stations to ensure accurate measurements for their designs. This ensures that plans are executed as intended, improving the efficiency of the design and construction process.
- Infrastructure Development: In projects like road and bridge construction, Total Stations are crucial for gathering accurate geographical data, which supports the structural integrity and safety of the constructions.
- Environmental Studies: Total Stations are utilised in environmental research, including climate change studies, by providing precise height and location data necessary for data analysis.
- Soil and Land Surveys: They are instrumental in analysing soil conditions, which aids in effective land development and management.
Conclusion
The use of Total Stations enhances accuracy and efficiency in surveying tasks, making them indispensable in modern construction and engineering practices. They integrate various functions that streamline the data collection process, thereby contributing significantly to the success of projects across different domains.
Uses of Total Station
Total stations are used for the following purposes:
- Measuring angles
- Measuring distances
- Measuring rectangular coordinates
- Measuring section lines
- Setting out measurements
- Setting out lines
- Point projection
- Measuring lost or omitted lines
- Data recording
- Registering/deleting data
- Measuring offsets
- Determining the area of a surface
- Selecting and deleting jobs
- Outputting job data.

What is Digital Surveying?
Surveying refers to the process of mapping or measuring land. Digital surveying specifically refers to the digital methods used in land surveying. This method allows for easy and accurate measurement of land. A variety of digital instruments are utilised in this type of surveying. In the past, traditional tools like chains and tapes were primarily used for surveys.
To conduct a digital survey, equipment such as theodolites, tripods, and prisms are necessary. In digital surveying, a compass is used to accurately determine the north line, which helps establish the north-south direction of the land, thus ensuring accurate measurements for the east-west and north-south orientations. The advantage of this approach is that it clearly indicates the angle of any structures and the angles of the boundaries, significantly reducing the chances of errors in subsequent work on the land.
Digital surveying provides precise measurements of the land, minimising the possibility of errors. It also facilitates the layout of buildings at the beginning of construction projects.
Moreover, digital surveying allows for accurate levelling of the land. Identifying elevated and depressed areas is crucial for land filling and excavation. By using digital surveying, one can easily calculate the amount of soil or sand required for filling land.
Digital Survey is a modern method that is highly effective for data collection, analysis, and design. It provides more accurate and efficient information through the use of technology.
Why Digital Surveys Are Conducted:
- Accuracy: The use of digital technology enhances measurement accuracy. Satellite and GPS technologies ensure high precision of data.
- Efficiency: Digital surveys allow for rapid data collection, saving time and reducing labour requirements.
- Data Analysis: The collected data can be easily analysed using computer software, assisting in decision-making.
- Remote Operations: With digital technology, it is possible to collect data from remote locations, helping to tackle environmental and geographical challenges.
- Versatility: Digital surveys are used in various fields, including geology, geography, construction, and environmental conservation.
How Digital Surveys Are Conducted:
- Planning: A plan for the survey area is created, identifying specific data and objectives.
- Equipment Selection: Necessary equipment for the digital survey, such as Total Station, GPS, and drones, is chosen.
- Data Collection: Surveyors use the selected equipment to gather geographical and environmental data.
- Data Analysis: The collected data is analysed, and maps or models are created using software.
- Report Preparation: A detailed report is prepared by compiling all data, which is helpful for future planning and decision-making.
Conclusion
Digital surveys represent a powerful method of modern data collection, crucial for accuracy, efficiency, and effective decision-making. They provide the foundation for necessary information across various industries.
What is the Purpose of Digital Surveying?
The primary aim of conducting this survey is to obtain accurate measurements of land. This is particularly important for lands that are not perfectly rectangular, as manually measuring such areas can lead to inaccuracies or complexity. In these cases, tools like Total Stations or Theodolites are used for precision.
- To determine the relative height or depth of various points or objects.
- To measure earthworks for roads, highways, irrigation channels, etc.
- To create contour designs and determine the volume of earth and the capacity of reservoirs.
- To establish permanent benchmarks in a specific area.
- To determine the preparation levels for roads or railways.
- To identify the maximum flood levels.
- To use levelling techniques for the plinth level, floors, roofs, etc., of buildings.
Importance of Digital Survey
Digital surveys are a highly effective modern method for data collection, particularly in fields such as construction, geography, environmental conservation, and engineering. Below are some key points highlighting the importance of digital surveys:
1. High Accuracy: Digital surveys use advanced technology like GPS and satellite systems, ensuring highly accurate measurements, which is crucial for precise project execution.
2. Increased Efficiency: The use of digital technology accelerates the data collection process, saving time and reducing the need for labour. This helps increase the speed of projects.
3. Ease of Data Analysis: Data collected through digital surveys can easily be analysed using computer software. This improves the decision-making process by providing clearer insights and models.
4. Application Across Various Fields: Digital surveys are applicable in diverse sectors, including construction, geography, geology, and environmental protection, making them versatile.
5. Remote Data Collection: With digital technology, data can be collected from remote or hazardous locations, making surveys more accessible and safer in challenging environments.
6. Timeliness of Information: Digital surveys provide real-time updates, enabling quick adjustments and decisions based on the latest data available.
Conclusion
Digital surveys are essential for improving accuracy, efficiency, and effective decision-making. They have become a foundational method of information gathering in various industries, establishing themselves as a powerful modern tool for data collection.
Importance of Digital Survey
1.Accurate Knowledge of Land Orientation: Digital surveys provide the opportunity for rapid data collection. They save time and reduce the need for labour, resulting in increased work efficiency. Additionally, digital surveys allow for quick updates of information, which aids in making prompt decisions for projects.
2.Data Collection for Various Features: Information about drains, culverts, box culverts, trees, power poles, ponds, elevated land, low land, buildings, semi-pucca houses, tin-shed houses, etc., can be easily analysed using computer software. This plays a significant role in decision-making.
3.Land Measurement: Measuring land and adjacent areas, along with essential road measurements, is crucial. The accuracy of measurements significantly increases with the use of digital technology. Satellite and GPS technology ensure high precision in data, which is particularly important for various projects. Furthermore, the locations of existing structures such as houses or trees on the land are also included in this data.
4.Identifying Elevation Changes: Digital surveys can identify contour changes on the land, especially in larger areas or in locations with dips and hills. The use of digital technology enables data collection from remote and hazardous locations, helping to address environmental and geographical challenges.
Conclusion
Digital surveys are essential for accuracy, efficiency, and effective decision-making. They form the basis for information in various industries, establishing themselves as a powerful method for modern data collection.
Advantages of Digital Surveying
Digital surveying allows for the accurate determination of any land’s location. It ensures precise identification of the north-south orientation of the land, measurements of the land itself, and surrounding areas, which is essential for road construction. Additionally, the locations of existing structures, trees, or other features on the land are documented.
If there are any elevations or depressions on the land, referred to as contours, this information is obtained through digital surveys. This is particularly important for larger plots of land or areas with depressions and hills. A digital survey must be conducted before any construction work begins. When planning a structure according to the survey report, there are no issues with the layout. Manual surveys may lead to errors due to the land’s curvature.
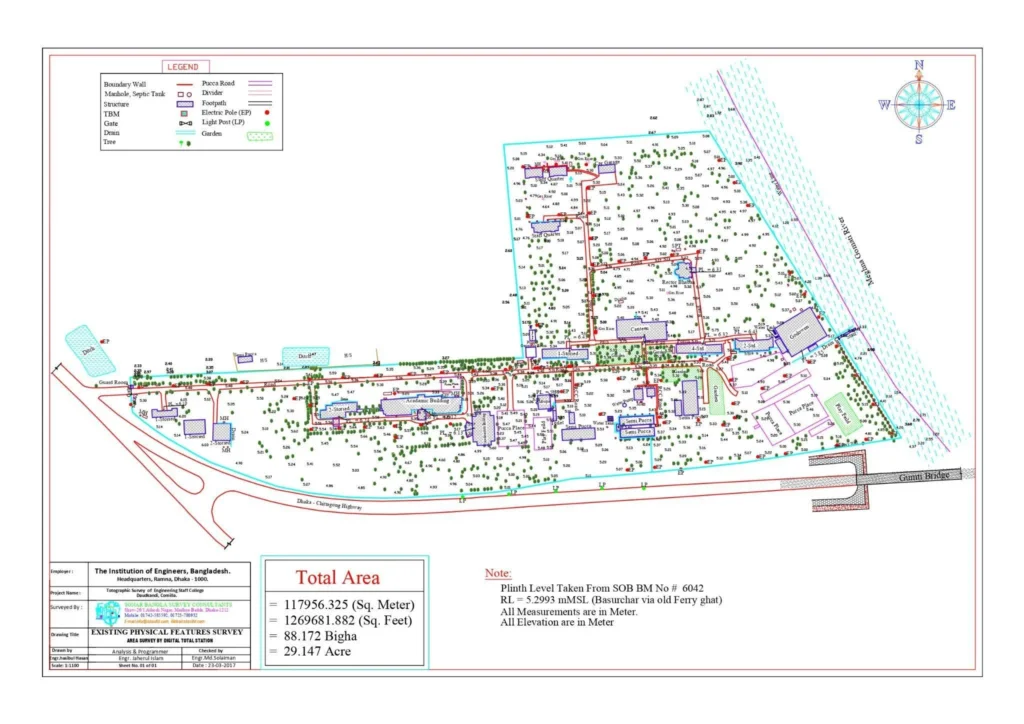
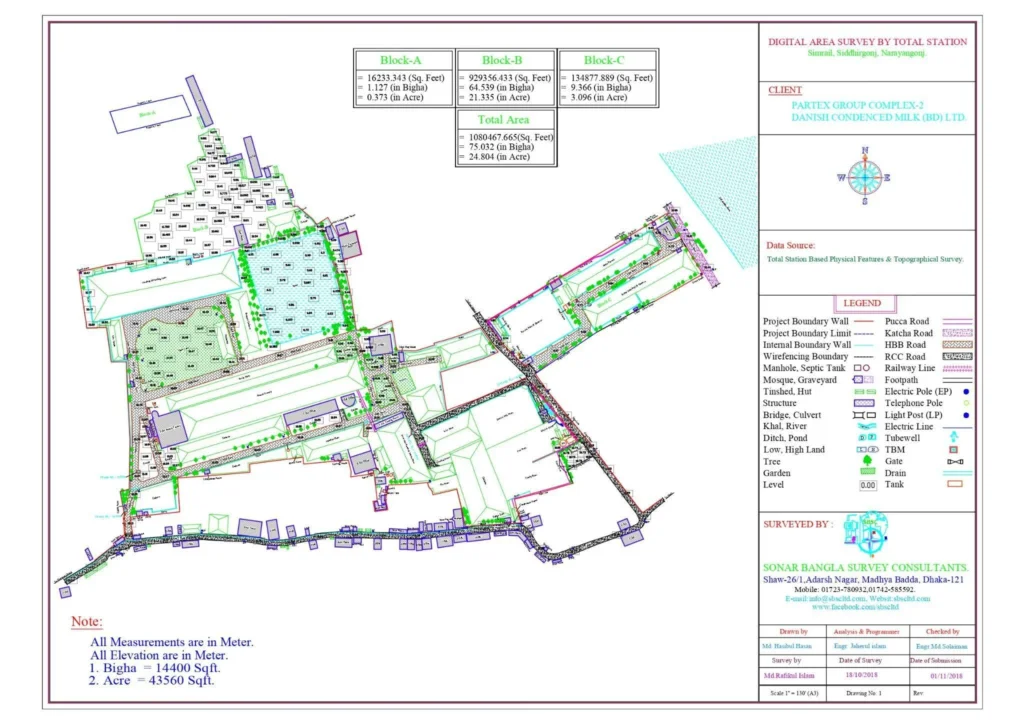
Digital surveys are conducted using total stations, which record all features both inside and outside the land, such as roads, electric poles, lamp posts, light posts, trees, buildings, semi-pucca structures, tin sheds, drains, spot levels, ponds, low-lying areas, elevated regions, canals, rivers, culverts, and buildings outside the property. This detailed documentation greatly facilitates the planning and design work for the land.
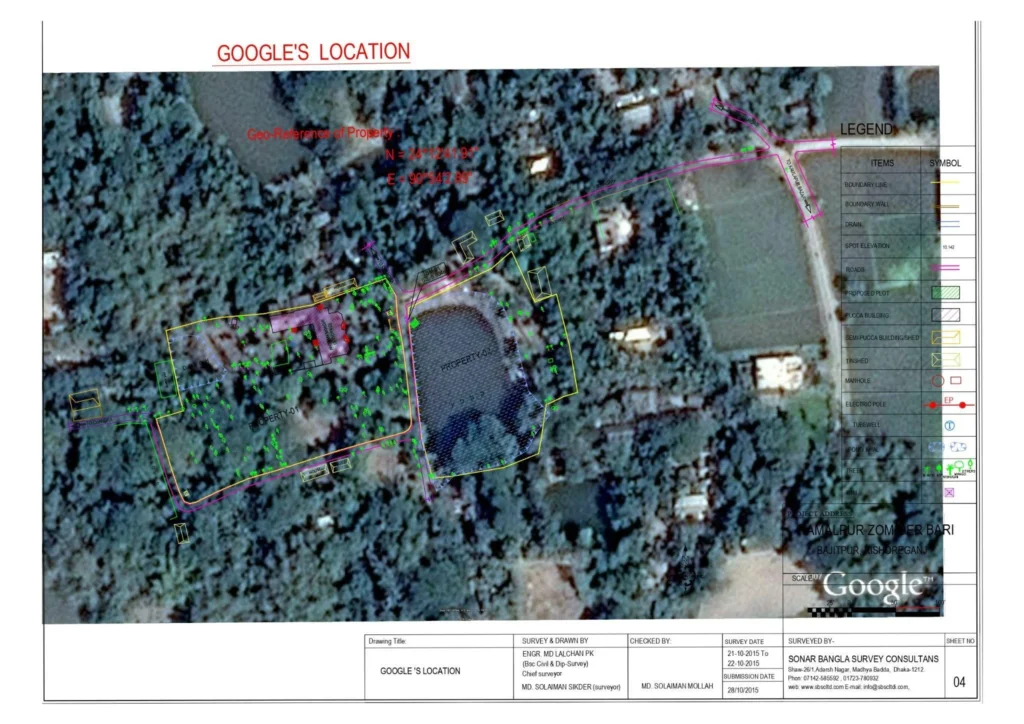
Digital Land Survey refers to the use of modern technology to accurately measure and map land areas. Unlike traditional land surveying methods, which relied on manual measurements and paper maps, digital land surveying uses advanced tools like Global Positioning Systems (GPS), Total Stations, drones, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect, store, and analyse data. This method provides precise, up-to-date information that is essential for various fields such as construction, urban planning, environmental conservation, and agriculture.
Key Components of a Digital Land Survey:
- High Accuracy: GPS and Total Stations offer extremely accurate land measurements, minimising human error and providing better data quality.
- Efficiency: The use of digital tools allows for faster data collection and processing, reducing the time and labour required in comparison to traditional methods.
- Data Storage & Analysis: Digital data can be easily stored and analysed using specialised software like AutoCAD or GIS platforms, helping in better visualisation and interpretation of the land features.
- Remote Sensing: Drones and satellite imagery allow surveyors to collect data from remote or difficult-to-access locations safely.
- Real-Time Updates: Data can be updated quickly, offering stakeholders the ability to track changes over time and make informed decisions rapidly.
Applications of Digital Land Survey:
- Construction: Accurate site mapping for infrastructure projects.
- Urban Planning: Developing city layouts and monitoring growth.
- Agriculture: Optimising land use and crop placement based on soil data.
- Environmental Studies: Monitoring land degradation, forest cover, and biodiversity.
Conclusion:
Digital land surveying enhances precision, efficiency, and versatility in various sectors, making it a valuable tool for modern land management and development.

What is a Land Survey?
Land surveying is the process of measuring and mapping land or areas, which is essential for any project. Land serves as the foundational asset for any project. Without accurate land measurements, engineering and construction projects cannot commence, as the land area may not always be a perfect rectangle or other regular shapes.
Manual land surveys often cannot produce accurate maps, especially if the land is uneven or irregular. Traditional methods using tapes and chains have various limitations and errors. As a result, digital land surveying has become increasingly important in Bangladesh and other countries.
Digital technology allows for precise measurement of land, reducing the likelihood of errors.
Digital land surveying can accurately measure any land, regardless of inconsistencies or variations in the terrain. It can determine the scale and accurately capture angles, showing the exact amount and dimensions of the land.” Digital land surveying offers significant advantages over traditional surveying methods. Its key characteristics include:
1. High Accuracy: Digital surveying uses technologies like GPS, GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System), and laser scanning to capture highly precise measurements of land. This precision is crucial for engineering, construction, and mapping projects.
2. Faster Data Collection: Digital systems streamline the survey process, significantly reducing the time required to gather data compared to traditional methods. Tools like drones and Total Stations allow surveyors to cover large areas quickly.
3. Minimised Errors: Automated digital tools reduce the human error common in manual surveys, leading to more accurate data collection and reliable results.
4. Real-Time Data Processing: Collected data can be processed and analysed immediately using specialised software. This allows for the creation of maps, 3D models, and detailed reports in real time, improving decision-making processes.
5. Remote and Difficult Terrain Access: Technologies like drones and satellite imagery allow surveyors to reach and survey areas that are remote, dangerous, or difficult to access on foot, improving safety and efficiency.
6. Versatile Applications: Digital land surveying is used across various fields, including urban planning, construction, environmental conservation, and land development. Its flexibility makes it applicable to both small-scale and large-scale projects.
7. Data Integration and Storage: The use of GIS (Geographic Information System) technology in digital surveys enables easy integration, analysis, and storage of large data sets, allowing for better project management and long-term access to information.
These characteristics make digital land surveying essential in modern infrastructure and development projects.
What makes the land survey so accurate?
“It stands for EDM, which means Electronic Distance Measurement. This technology uses computerised techniques to measure angles, distances, and elevations. Such measurements cannot be achieved with a standard tape measure survey. The Total Station is the land surveying instrument we use to incorporate EDM. These machines have created a new trend in measuring land and buildings. Similarly, they help maintain the accuracy of layouts in large construction projects.
In massive constructions like bridges and flyovers, Total Stations collect data on distances, angles, and levels with great precision. Cadastral or property surveys are conducted to establish accurate locations, boundaries, or subdivisions of land within a specific area. Additionally, such surveys require a professional and registered specialist in all states.” Total Stations are crucial tools in land surveying, providing high accuracy through several key features and methodologies:
1. Integrated Measurements: A Total Station combines the functionalities of an electronic theodolite for measuring angles and an electronic distance measuring (EDM) device for measuring distances. This integration allows for simultaneous measurement of horizontal and vertical angles along with distances, resulting in precise coordinates for any point in the survey area.
2. Automatic Data Recording: Total Stations automatically record measurements, which reduces human error associated with manual data entry. This capability ensures that data is collected consistently and accurately, allowing for reliable analysis and reporting.
3. Real-Time Feedback: Many modern Total Stations offer real-time feedback during the surveying process, enabling surveyors to verify measurements as they work. This immediate feedback helps identify potential errors on-site, allowing for corrections to be made instantly.
4. GPS Integration: Some Total Stations can integrate GPS data, which enhances positioning accuracy, especially in large areas or difficult terrains. This integration ensures that the coordinates obtained from the Total Station can be correlated with global positioning systems for enhanced accuracy.
5.Advanced Software: Total Stations often come equipped with software that helps process the collected data. This software can perform calculations, generate topographic maps, and create 3D models. Advanced data processing minimises errors and enhances the accuracy of the final survey results.
6. Calibration and Maintenance: Regular calibration of Total Stations is essential to maintain their accuracy. Surveying professionals ensure that the equipment is correctly calibrated before use, further enhancing the reliability of the measurements taken
Tasks of Digital Land Surveying
- Establishing markers or monuments that can define the report and, as a result, preserve the boundaries of the land.
- Reestablishing old land survey lines to determine their lengths and orientations.
- Due to the high value of the land, old lines are remeasured to obtain more accurate measurements, calculating area, distance, and directions.
- Preparing land maps to illustrate survey data so that they can serve as a permanent record.
- Writing a technical description of the work.

What Type of Land Survey is Best for You?
The type of land survey that is best for you depends on various factors, such as the purpose of the survey, the type of land, and your specific needs. Here are some common types of land surveys and their uses:
1.Topographic Survey: This survey provides detailed information about the land’s elevation, slope, and features. It is very useful for construction projects, land development, and environmental studies. If you need to know the characteristics of the land for project planning, this is a good choice.
2. Boundary Survey: If you need to determine the exact boundaries of your property, a boundary survey is crucial. It identifies the limits of the property and reveals any potential issues.
3. Cadastral Survey: This is necessary for land ownership and registration. It determines the boundaries and measurements of land parcels, which are required for legal documents.
4. Construction Survey: This helps in accurately laying out structures in construction projects. It aids in ensuring precision during the construction phase.
5.ALTA/NSPS Survey: This is a comprehensive survey for commercial real estate transactions. It provides detailed information on property boundaries, developments, and any potential issues.
6. Hydrographic Survey: If your land has water bodies, this survey helps depict underwater features.
7. Geodetic Survey: Used for precise measurements over large areas, it is critical for creating national maps.
To determine the right type of land survey for you, consider your specific needs, such as legal requirements, development plans, or environmental assessments. Consulting with a professional land surveyor can also provide valuable insights for your situation
Additionally, we conduct a specific type of land survey based on the intended use of the land. Specifically, Sonar Bangla Survey Consultants strive to meet client needs based on their expertise and land use. Accordingly, we offer to conduct all these types of digital land surveys based on purpose and usage:
- Topographic Survey
- Contour Survey
- Township Survey
- Road Survey
- Control Survey
- Levelling Survey
- Route Survey
- Compass Survey
- Set-Out Survey
- RTK GPS and GPS Survey
- Hydrographic Survey
- Traverse Survey
- Railway Survey
- Pipeline Survey
- Canal Survey
- Building and Construction Survey
- Transmission Line Survey
- Layout Design Survey
- GIS Survey
- Bridge Survey.
Describe the Different Type of Projects Such As:
(a) Irrigation Project (b) Hydrographic project (c) Sewer pipe line project
(d) Tunnel Project
Translate English give me the grammatical correct version”
Survey Work Involved in Irrigation Canal Project
The various survey works associated with the irrigation canal project are as follows: (i) Reconnaissance Survey
(ii) Preliminary Survey
(iii) Detailed Survey
(iv) Construction Survey
Description of Reconnaissance Survey
This survey is conducted very rapidly along the proposed route over the entire area. The survey along the proposed alignment is carried out quickly using lightweight instruments such as a prismatic compass, tape, and hand level. After completing this type of survey, the engineer must provide information in the form of a reconnaissance report, which includes the following examinations:
(i) Topography of the project area.
(ii) Potential alignments.
(iii) Significant areas, cities, rivers, hills, etc.
(iv) Soil and drainage conditions.
(v) Maximum flood level.
(vi) Availability of labour and construction materials.
(vii) Land value.
(viii) Required time for construction work.
(ix) Amount of high and low areas.
(x) General slope of hilly areas.
The essential information that must be collected regarding the topography along the alignment includes: (i) Direction of river flow.
(ii) Water surface level.
(iii) Slope of the waterway.
(iv) Amount of earth excavation.
(v) Cost of earth filling.
(vi) Number of bridges, etc.
Conclusion
As you stand atop a hill, gazing out at the undulating landscape, you’re reminded of the ancient Greek myth of Daedalus, who mastered the art of traversing complex labyrinths.
Similarly, a contour survey is your map, guiding you through the twists and turns of the terrain.
With its precise measurements and intricate lines, it’s your key to deciphering the secrets of the land, ensuring your construction projects are built on solid ground.
For a professional and accurate contour survey, call Sonar Bangla Survey Consultants office at +880 1742 585592 to get a free quotation from a team with a proven track record of excellence, boasting over 150 5-star reviews on Google.

