What is meant by Hydrographic Survey?
Hydrographic survey refers to the branch of surveying that deals with the study of underwater terrain, area, water flow, water volume, water depth, and all related aspects of water bodies such as seas, oceans, rivers, canals, reservoirs, and ponds.
What is the meaning of the word “Hydro”?
The word “Hydro” means water.
What topics are included in hydrographic surveys?
Hydrographic surveys encompass several important topics that are essential for analyzing the characteristics and flow of water in climates, rivers, water bodies, and oceans. Below are the main topics of hydrographic surveys:
- Water Level Depth and Changes
- Measurement of the depth of water bodies, rivers, or oceans.
- Monitoring changes in water levels, such as rises and falls.
- Water Flow Velocity
- Determination of the flow velocity of rivers and water bodies.
- Measurement of flow volume and capacity.
- Water Quality Analysis
- Measurement of water quality parameters, such as pH, temperature, acidity, and pollution levels.
- Analysis of various pollutants, such as nitrates, phosphates, and coliform bacteria.
- Bottom Characteristics
- Determination of the structure and characteristics of the river or water body’s bottom.
- Navigation of materials such as sand, gravel, or other bottom elements.
- Climate Change
- Analysis of the impacts of climate change and the resulting changes in water levels.
- Evaluation of the effects of natural and human-induced factors.
- Navigational Safety
- Creation of maps for safe navigation routes for vessels.
- Identification of hazardous areas.
- Water Resource Management
- Effective use of water resources for supply, irrigation, and other purposes.
- Pollution control and water protection planning.
These topics in hydrographic surveys are extremely important for water resource management, aiding in environmental conservation, water management, and climate research.

Purpose of Hydrographic Survey
The objectives of a hydrographic survey are as follows:
(i) To determine the highest and lowest positions of the waterbed.
(ii) To analyze the velocity, direction, and characteristics of water flow.
(iii) To assess the discharge capacity of rivers and streams.
(iv) To perform soundings and determine the characteristics of the waterbed.
(v) To identify obstacles like buoys, lighthouses, submerged mountains, sandbars, etc., for the safety of navigation.
(vi) To estimate the volume of earthwork for dredging operations.
(vii) To monitor the coastline design and any changes in its position and direction.
(viii) To gather relevant information for projects like bridges, dams, tunnels, reservoirs, docks, and harbors, and assess their feasibility.
(ix) To evaluate the feasibility of water irrigation, flood control, water development, conservation, and supply projects.
(x) To prepare a navigability list and ensure waterway depth is suitable for navigation.
(xi) To determine and identify areas of soil erosion and sediment deposition underwater.
Shoreline Survey
The shoreline survey typically involves three tasks:
(i) Determining the shoreline.
(ii) Identifying and marking the location of important reference points on the shore used in soundings.
(iii) Determining the position of the highest waterline.
Shore line Survey
Shoreline surveys are typically conducted by using a tape measure to take offsets from the boundary line on the beach to the water’s edge, or by employing a stadia or plane table to determine the shoreline. Objects that are clearly visible from the water surface, such as lighthouses, tall minarets, and church steeples, are marked as reference points on the design through triangulation surveys. The highest water level can be approximately indicated by features like marks on rocks and silt lines. To obtain accurate results, the average highest water level can be used to directly contour the shoreline on the design. Furthermore, the connecting shoreline between the low and high water marks can be determined through soundings.
River Survey
In a river survey, the riverbank is determined by using a transit theodolite and tape at a convenient distance from the water flow. Where the riverbank curves, the position of the shoreline is identified using offsets from the chain line or with the aid of a plane table or stadia survey. If the river is narrow, the positions of both banks can be depicted on the design using a tachometric survey or plane table from the chain line of one bank. In cases where the river is wide, the shoreline is delineated on the design through separate surveys of both banks. For inspection, the chains from both banks are measured at specified intervals, using cross bearings or angles for alignment.
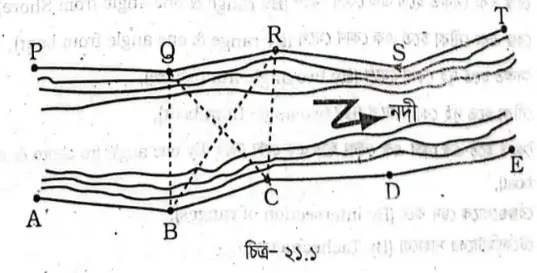
In the diagram, the chain on one bank is labeled PQRST, and on the opposite bank, it is labeled ABCDE. To verify, angles ∠QBR, ∠RBC, ∠ZRCQ, and ∠QCR can be measured from points B and C, and the length of QR can be determined by measuring the length of BC. If the length of QR matches its actual length, then QR is deemed accurate in the survey. If there are forests or jungles along the riverbank, making it impossible to establish a chain line, verification can be done by measuring the baseline through triangulation surveying.

What are the main features of hydrographic maps?
Some key features of hydrographic maps are listed below:
Water Level Depth
The depth of water bodies, rivers, and oceans is indicated on the map. Depth is usually represented using contour lines or bathymetric contour lines.
Water Flow Direction
The speed and direction of river flow are noted, which is important for navigation.
Boundaries of Water Bodies
The boundaries of various water bodies, such as lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, are clearly marked.
Dams, Navigation Routes, and Ports
Information about the locations of dams, navigation routes, and ports is included on the map, which aids in marine transport and water resource management.
Diverse Information
Indicators for water quality, temperature, and other scientific data may be present.
Navigational Safety
Safe navigation routes are identified, along with hazardous areas or danger zones.
Local Infrastructure and Land Use Information
The map may contain details about surrounding infrastructure and land use, such as industrial areas, residential areas, and agricultural land.
Seasonal Changes
Some hydrographic maps are prepared considering seasonal changes and variations in water levels.
Bottom Structure and Condition
The structure of the water body’s bottom, such as sand layers, gravel, and the locations of other materials, is identified.
Specialization and Updates
The map can be updated for specialization and corrections to include accurate and new information.
Hydrographic maps play a crucial role in water resource management, environmental conservation, and climate research.
Write Four Objectives of Hydrographic Survey.
The objectives of hydrographic survey are described below:
(a) To determine and study the changes in the shoreline, the history of disputes along the coastline, and their altered conditions over time.
(b) To create a design of the coastline.
(c) To conduct soundings and determine the characteristics of the seabed.
(d) To identify areas where rock, sandbanks, or sediment have accumulated on the seabed, and where land erosion is occurring.
List the Instruments Used in Hydrographic Survey.
The list of instruments and related equipment used in hydrographic survey is as follows:
(a) Sounding Boat
(b) Sounding Rod or Pole
(c) Lead Line
(d) Sounding Lead
(e) Sounding Machine
(f) Fathometer or Echo Sounder
(g) Sextant
(h) Signal
(i) Cross Rope
(j) Sounding Chain
(k) Water Telescope
(l) Station Pointer
What is Sounding?
The process of measuring the vertical depth of water from the water surface to the seabed is called sounding. Just as the roughness of the land is determined using leveling techniques on land, sounding is used to determine the roughness of the seabed in waterlogged areas. This is done by measuring the depth of water at various points from a boat.
What is the Main Purpose of Sounding?
The primary purpose of sounding is to determine the topography of the underwater terrain and to identify submarine contours. The main objectives of sounding are to ascertain the depth of water and the characteristics of the seabed. It is used for various purposes, such as:
Determining Depth:
Sounding is used to measure the depth of water bodies, rivers, or oceans, which is crucial for navigation and fishing.
Understanding Seabed Characteristics:
Sounding data helps in understanding the composition of the seabed, such as the location of sand, rocks, and other materials.
Navigation Safety:
Sounding information is utilized to identify safe navigation routes to prevent vessels from entering hazardous areas.
Environmental Analysis of Rivers and Water Bodies:
Sounding data is used to analyze the environmental conditions of rivers and water bodies, which is helpful in understanding the impacts of climate change.
Land Management and Development:
By understanding local land characteristics through sounding, planning for land management and development projects can be effectively executed.
Water Resource Management:
Sounding data is used to create effective management and conservation strategies for water resources.
These objectives of sounding are essential for ensuring effective water resource management, environmental conservation, and maritime safety.
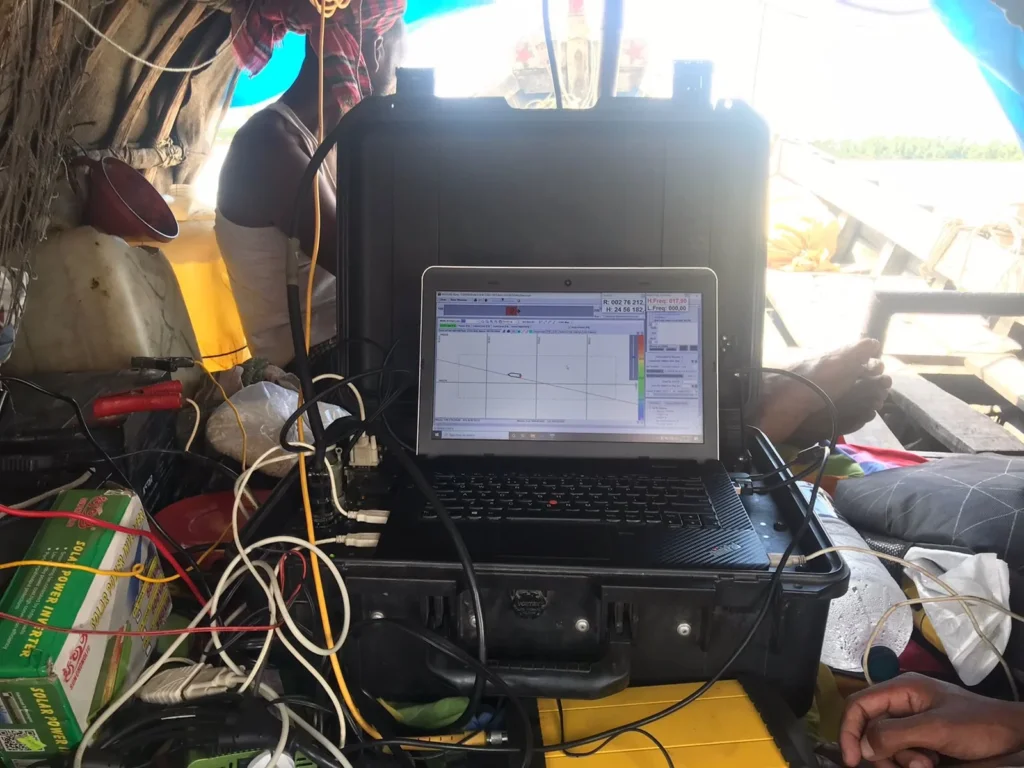

Purpose of Sounding:
(1) To determine the underwater topography or undulations of a river or any water body.
(2) To create a navigational chart for waterways.
(3) To calculate the volume of dredged soil and determine the areas where dredging will occur and where it will be disposed of.
(4) To assess the drainage capacity of rivers or canals.
(5) To evaluate the holding capacity of lakes or any enclosed water bodies.
(6) To conduct soundings for designing various structures in harbors, such as breakwaters, sea walls, and wharves.
When sounding is conducted using a lead line, the method may vary based on the water depth and current. If the depth does not exceed 25 meters, there is no need to stop the boat. The sounding lead is thrown forward in such a way that it reaches the bottom as the moving boat arrives at the sounding point, keeping the lead line vertical, and the sounding is taken at that moment.
It is essential to record the location of sounding, the date, the observer’s name, the designation of the raising line, the sequential number of soundings along the raising line, the time, the angles (for sextants), the observed point on the bank, the depth of each sounding, the water level gauge readings, and any corrections to the sounding line. When measuring angles from the bank, it is necessary to document the sounding, azimuth, time, bearing, serial designation, and any other relevant information
What is meant by “Control”? What are its types?
In order to conduct a hydrographic survey efficiently, the horizontal or vertical distances measured from various reference points established by triangulation in the survey area are referred to as controls.
It can be classified into two types, namely:
১। horizontal control.
২। vertical control.
What is meant by horizontal control and vertical control in hydrographic surveying? Why and how is it done?
Horizontal Control: Just like in topographic surveys, hydrographic surveys measure the azimuth and length of several sequentially connected arms. This is referred to as horizontal control. It helps establish the framework for the survey area and aids in the detailed design plannin
Vertical Control: Vertical control refers to the vertical distances measured from the benchmark (BM) or other reference points to sequentially established reference points at regular intervals, using spirit leveling along riverbanks or coastal areas.
What is a Shoreline Survey? Why is it conducted?
A Shoreline Survey refers to the process of analyzing the coastline or shorelines of the sea, including the shape, characteristics, and changes of the land. It primarily pertains to the area that serves as the boundary between land and water (such as the sea, lakes, or rivers).
Reasons for Conducting Shoreline Surveys:
- Land Management:
Surveys are conducted to manage changes along the shoreline and the surrounding land, allowing for the planning of coastal development and protection activities. - Environmental Conservation:
Shoreline surveys are essential for preserving the health of coastal ecosystems, which is vital for the biodiversity of various species. - Safety of Navigation:
Surveys help identify safe navigation routes and pinpoint hazardous areas, ensuring that vessels can operate safely. - Impact of Climate Change:
Surveys monitor changes occurring in coastal areas due to climate change, providing data for future planning. - Water Resource Management:
Shoreline surveys ensure the proper management and utilization of water sources and resources. - Planning for Various Projects:
Surveys are necessary for planning various projects in coastal areas, such as tourist centers, industrial zones, and infrastructure development.
In conclusion, shoreline surveys are a crucial process that aids in the management of our environment, land, and water resources.
The shore line survey is conducted for the following reasons:
- To determine the shoreline.
- To identify the locations of various important topographic features or landmark points on the shore, such as the spires of mosques, temples, and churches, lighthouses, windmills, and GTS pillars.
- To establish the maximum and minimum water levels
The three objectives of sounding are:
- To prepare a list of navigation routes.
- To determine the drainage capacity of a river or canal.
- To assess the storage capacity of a pond or water body.
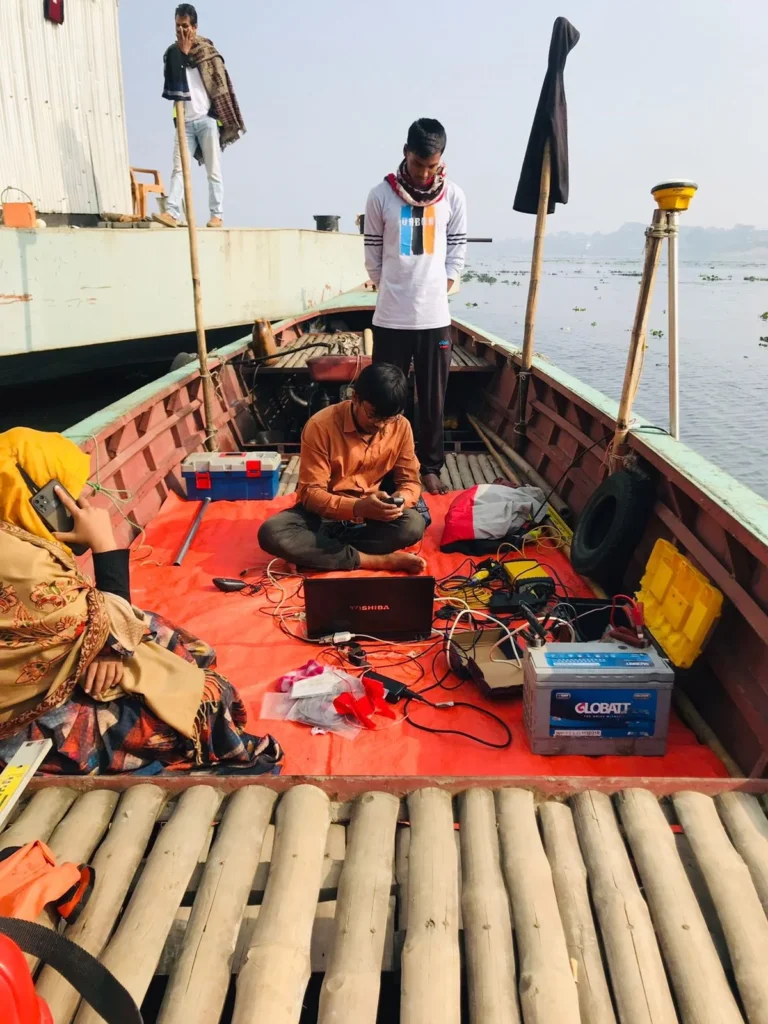

What is the necessity of sounding?
Sounding is performed for the following purposes:
- Determining Depth:
Sounding is used to determine the depth of water bodies, rivers, or seas, which is essential for vessels and fishermen. - Navigational Safety:
Safe navigational routes are identified using sounding data, and dangerous areas are marked to ensure that vessels can operate safely. - Understanding Bottom Characteristics:
Sounding provides information about the composition and features of the seabed, such as sand, gravel, rocks, etc. - Vessel Efficiency:
Sounding helps in planning effective routes for vessels, allowing them to navigate safely and accurately. - Sounding for Ponds:
Sounding is a crucial process for determining the capacity of ponds or water bodies. It establishes the capacity of a water body through the analysis of water depth and bottom characteristics. - Volume Calculation:
The volume of a water body is determined using data from various depths. Typically, the following formula is used to calculate the volume of a pond:
V=A×DV = A \times DV=A×D
where VVV is the volume, AAA is the surface area of the water body, and DDD is the average depth.
- Bottom Features:
The composition of the seabed, such as sand, gravel, rocks, etc., is identified through sounding, which affects the capacity of the water body and changes in water levels.
What is meant by echo sounding?
Echo refers to the phenomenon of reflection. The method of sounding that uses sound waves generated at the water’s surface, which then reflect off the riverbed to create a continuous profile of the riverbed, is known as echo sounding
What is meant by a fathometer?
A fathometer is a type of electrical instrument used for sounding in oceans or seas. It measures the time interval between the transmission of sound waves to the seabed and the reception of their echo to determine the depth of the ocean.
What is meant by soundings reduction?
The rise and fall of tides or the surface of a water body with currents are not always stable; they fluctuate. As a result, it is not possible to take soundings from the same height of water at different points. For this reason, a gauge reading is taken at the time of sounding at each point. The process of determining the value of sounding at each point by applying gauge corrections with the obtained gauge readings and soundings relative to a specific datum level is called soundings reduction.
What is meant by river survey?
Answer: The river survey involves establishing a traverse along the riverbank at a convenient distance from the water surface using a transit theodolite and tape. If the riverbank is winding, offsets are taken to determine the positions of points using stadia or plane table methods, allowing for the drawing of the design. In the case of wide rivers, a traverse is conducted from one bank, and both banks’ designs are drawn using stadia or plane table surveying.
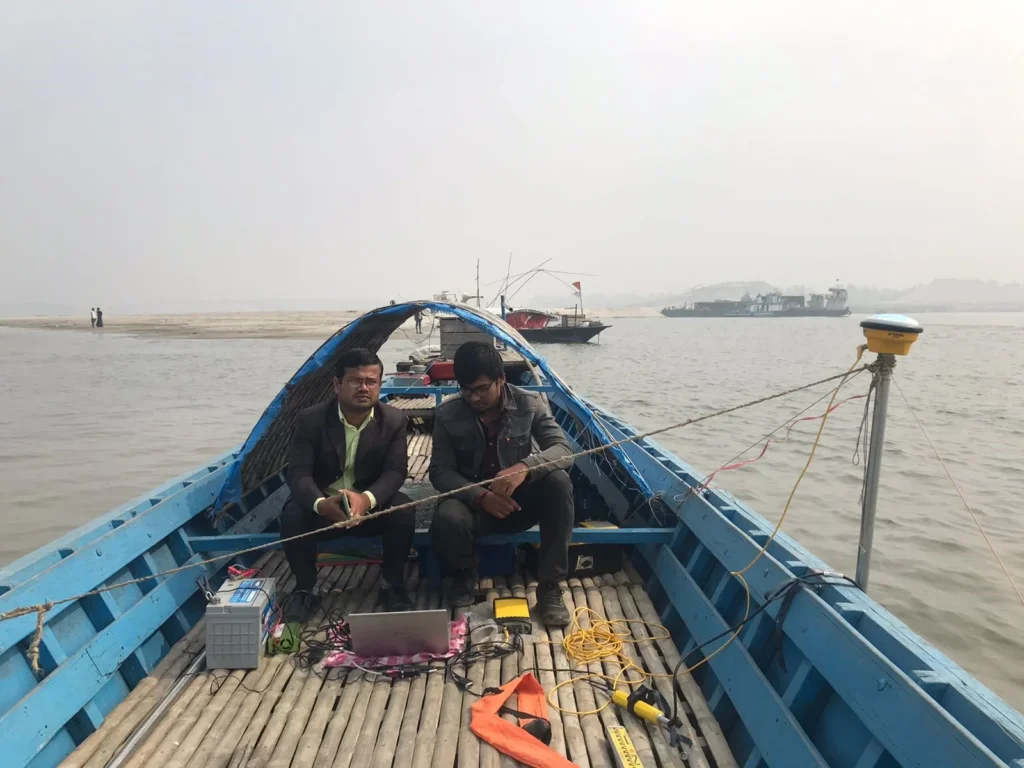

What is a Hydrographic Survey?
Additionally, a hydrographic survey works with the topography of submerged areas such as rivers, canals, ponds, seas, and oceans. It also measures the area, water volume and levels, flow rates, the position of measurement points, and prepares a stowage list. Similarly, a hydrographic survey is a fundamental task for docks, harbors, coastlines, hydro energy, and water supply
What is the Purpose of a Hydrographic Survey?
- Similarly, determine the position of the coastline and observe changes in direction.
- Observe the origin and changes of the shoreline.
- Identify soil erosion, quantify sediment, and mark its area.
- Conduct soundings to determine the characteristics of the seabed in submerged areas.
- Calculate the depth of water for navigation, which is crucial for determining the volume of dredging required for navigability.
- Determine the direction and velocity characteristics of water flow.
- Assess the discharge capacity of rivers.
- Determine the average sea level and monitor tidal times.
- Specifically, identify the positions of buoys, lighthouses, shoals, and mountain ranges to clarify navigation safety.
- Establish the maximum and minimum levels of the water surface.
- Establish the contours and cross-sectional areas of submerged areas.
- Determine the capacity of enclosed water bodies.
Importance of Hydrographic Survey:
- Ensuring Navigation Safety: Hydrographic surveys identify safe navigational routes and hazardous areas, which is crucial for the movement of ships and other watercraft.
- Determining Seafloor Characteristics: It provides information about the structure of the seafloor in seas, rivers, or other water bodies, which is essential for determining navigability, dredging, and construction planning.
- Port and Waterway Development: Through the survey, the depth of ports and the usability of waterways are determined, which is vital for port expansion and development planning.
- Monitoring Coastal Erosion and Environmental Impact: Hydrographic surveys help in determining the changes in coastal areas and river sedimentation, which is necessary for environmental protection and preventing land erosion.
- Water Resource Management: By determining the water flow, level, and depth, hydrographic surveys aid in effective water resource management and planning.
- Tidal and Flood Control: The data from hydrographic surveys play a significant role in predicting and controlling tides and flood situations.
- Engineering and Construction Projects: Hydrographic surveys help in the proper planning of various construction projects like dams, bridges, and other reservoirs.
- Dredging Planning: By identifying the depth of the water bodies, hydrographic surveys help determine where dredging is necessary to increase navigability.
- Tourism and Recreational Activities: Hydrographic surveys are highly effective in water resource management for tourist destinations, beaches, and other recreational areas.
The method of hydrographic survey in rivers is a process by which the riverbed, flow, depth, and other characteristics are accurately determined. Through this survey, essential data for river water resource management, navigation safety, and environmental analysis are collected. The hydrographic survey in rivers is conducted in the following steps:
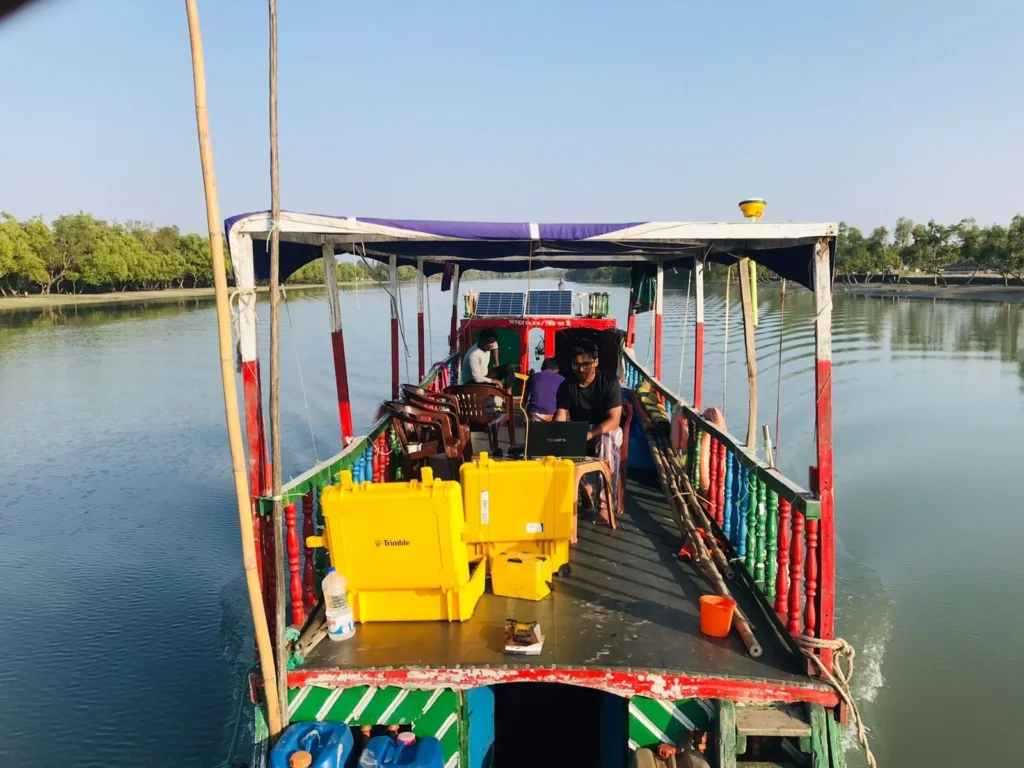

1.Initial Planning:
- Defining the Survey Objectives: The survey’s purpose determines which parts of the river will be surveyed, such as identifying navigation routes, studying the riverbed features, or collecting data for water resource management.
- Selection of Equipment: Equipment like echo sounders, GPS, and other hydrographic instruments are selected for the survey.
- Site Selection: Key points of the river where data collection is necessary are identified.
2. Conducting the Survey:
- Echo Sounding Method: Echo sounders are used to measure the river’s depth. Sound waves emitted by the echo sounder hit the riverbed and reflect back, and the time taken for this reflection helps determine the depth.
- GPS Usage: A Global Positioning System (GPS) is used to determine the exact coordinates of each survey point in the river.
- Data Collection: Information is collected on the riverbed’s structure, depth, water flow speed, and flow direction.
- Bottom Survey: The characteristics and structure of the riverbed (such as sand, rocks, or sediment) are identified, which is crucial for navigation or dredging.
3. Data Analysis and Map Creation:
- Data Processing: Data collected from the survey are processed to create topography and contour maps of the riverbed.
- Mapping: Hydrographic maps of the river are created based on the collected information, which can be used for vessel navigation, port construction, or water resource management.
4. Report Preparation:
- Analyzing Results: A report is prepared by analyzing the survey results and the condition of the river.
- Recommendations: The report provides recommendations for the riverbed’s structure, navigation safety, dredging needs, and water resource management.
5. Practical Applications:
- Navigation: The information is used to identify safe navigation routes.
- Dredging Planning: It helps determine where dredging is required to increase the navigability of the river.
- Environmental Conservation: The data from the hydrographic survey is utilized to monitor environmental changes and sedimentation in the river.
By using this method, accurate information about the riverbed and water resources can be obtained, which is essential for safe navigation, water resource management, and environmental conservation.
What is meant by an offline hydrographical survey?
Moreover, a hydrographic survey is the science of measurement that can influence marine navigation, marine construction, dredging, offshore oil exploration/offshore oil drilling, and related activities. Therefore, conducting an accurate hydrographic survey is of utmost importance. Additionally, our company provides high-quality hydrographic survey services that cater to the various needs of our clients. In such surveys, we study the physical characteristics, distribution, circulation, and volume of water bodies. Similarly, we employ the latest instruments and advanced techniques to provide these services.
Conclusion
As you stand atop a hill, gazing out at the undulating landscape, you’re reminded of the ancient Greek myth of Daedalus, who mastered the art of traversing complex labyrinths.
Similarly, a Hydrographical survey is your map, guiding you through the twists and turns of the terrain.
With its precise measurements and intricate lines, it’s your key to deciphering the secrets of the land, ensuring your construction projects are built on solid ground.
For a professional and accurate contour survey, call Sonar Bangla Survey Consultants office at +880 1742 585592 to get a free quotation from a team with a proven track record of excellence, boasting over 150 5-star reviews on Google.

