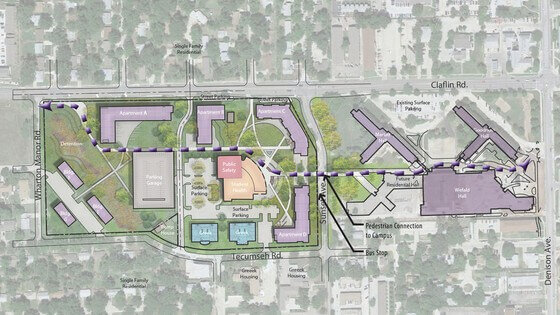
What is a master plan design?
Additionally, A Master plan Survey is a long-term plan. that provides a vision and framework for how an area.
A master plan Survey is an overarching planning document and spatial layout. Developers use it to structure land use and development.
Master plans for a building site or land area are the long-term planning documents. that provide the concepts and guides for future growth and development.
Similarly, they cover not only the current existence but also future planning. In fact, in a large long-term project they may include several years. Specifically, Worth of development changes over time and the methods for transitioning from each stage to the next. Additionally, A good master plan would include a key plan, site plan, building plan and service plan, if not several.
Furthermore, with a small house the master plan might just be “we have an empty lot. Similarly, we’re putting a house on it”. Moreover, for a large complex of property the master plan might be several years’ worth of changes involving many buildings on the site.

What is a Master Plan Design?
A master plan design is a comprehensive framework or outline that provides strategic guidance for the development of a specific area or project. It is typically created for cities, urban areas, or special projects, and includes planning for land use, infrastructure, transportation, services, and other critical elements.
Main Components of a Master Plan:
- Land Use: Determining the use of land for various areas, such as residential, commercial, industrial, and recreational zones.
- Transportation System: Planning for roads, railways, and public transport networks.
- Social Infrastructure: Identifying locations for educational institutions, hospitals, parks, and other public amenities.
- Environmental Planning: Developing strategies to protect natural resources, wetlands, and other environmental elements.
- Economic Development: Creating policies and plans to enhance the local economy.
Objectives of a Master Plan:
- Focused Development: Ensuring integrated and planned development.
- Efficient Resource Use: Providing a plan for the efficient use of land and other resources.
- Public Benefits: Enhancing amenities and services for citizens.
- Forward-Looking Planning: Preparing for future needs and changes.
A master plan is an essential tool used for sustainable development, urban planning, and social and economic progress.

What are the contents of a master plan?
Likewise, A Master Plan Survey includes analysis, recommendations, and proposals for a site’s population, economy, housing, transportation, Community Facilities, and land-use
What is a Master Plan for a Site?
Specifically, the site master plan survey is an elementary plan that shows overall development based on a conceptual study. However, Defining the initial requirements of building spaces, flows. Likewise, Connections between buildings, logistics, urban design, infrastructures, and ancillary facilities, among others.
A master plan for a site is a detailed and integrated design that provides a strategic outline for the development and use of a specific land area. It highlights how the site will be organised, including land use, infrastructure, and service planning, in order to achieve the goals of the area.
Key Components of a Site Master Plan:
- Land Use Determination:
- Determining the land use for different regions of the site, such as residential, commercial, industrial, and recreational areas.
- Infrastructure Planning:
- Designing the essential infrastructure of the site, such as roads, utilities, drainage systems, and public amenities (like schools and parks).
- Transportation Connectivity:
- Planning the roadways, public transport routes, and pedestrian paths for vehicle flow and connectivity within the site.
- Environmental Considerations:
- Developing strategies to ensure environmental protection and sustainability, such as preserving green spaces, managing water resources, and minimising the impact on nature.
- Public Amenities:
- Planning spaces for parks, recreational areas, and other public facilities to enhance services for citizens.
- Phased Development:
- Establishing a timeline and phases for site development that allows for growth and changes according to demand and resources.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensuring that the master plan aligns with local zoning laws, building codes, and other regulatory requirements.
Objectives of a Site Master Plan:
- Vision and Direction: Providing a clear vision for the future development of the site and guiding the decision-making process.
- Coordination: Facilitating coordination among various stakeholders, including developers, government agencies, and the community.
- Sustainable Growth: Implementing sustainable development that balances economic growth with environmental protection.
In summary, a master plan for a site is an essential tool that aids effective planning, ensures organised land development, and protects community needs and natural resource

What are the functions of master planning?
Likewise, A master plan survey lays out the goals and objectives of the institution, documents existing conditions through a site and/or facilities analysis. But also, Presents the current and projected needs of the client along with a conceptual configuration for the project.
Master Plan Scale Model
Additionally, Make Master Plan Models for Large Landscape, City with …
Master plan survey models are usually made for visionary people and master developers. Similarly, who plan to transform barren land to a large community. Shoreland to waterfront development and even artificially created waterfront developments on mainland.
What is Layout plan/Survey?
Likewise, Layout planning is deciding on the best physical arrangement of all resources that consume space within a facility. But also, these resources might include a desk, a work centre, a cabinet, a person, an entire office, or even a department.
What is a Layout Survey?
Similarly, a construction layout survey is typically associated with the layout of new facilities or earthworks. Consequently, point locations or reference points are determined from the provided engineers’ drawings and are set in the field to guide the construction of new structures, roads, and utilities.
Key Aspects of Layout Survey:
- Site Measurement:
Accurate measurements are taken to determine the site’s boundaries, topography, and existing features. - Positioning of Structures:
The locations of proposed structures, such as buildings, roads, and utilities, are identified and marked based on architectural and engineering plans. - Coordinate System:
A coordinate system is established according to local geodetic standards, ensuring measurement accuracy and consistency. - Reference Points:
Reference points and benchmarks are established on-site, which will aid in future construction and layout activities. - Documentation:
Detailed drawings or maps are created to show the site layout, including dimensions, directions, and the locations of all components.
Objectives of a Layout Survey:
- Accuracy in Construction:
Ensures that construction activities are carried out correctly according to the design plans. - Regulatory Compliance:
Helps to ensure that the correct positioning of structures and infrastructure aligns with local zoning and building regulations. - Conflict Resolution:
Identifies potential conflicts with existing utilities or features, allowing for adjustments before construction begins. - Project Planning:
Assists in the overall planning and coordination of construction projects, ensuring that all stakeholders agree on the site layout.
In summary, a layout survey is a crucial step in planning and executing construction projects, providing the necessary information and structure for accurate and effective development.

What is a key plan?
Key plans are the individual floor plans showing primary architecture elements for each floor of a structure. But also, they graphically represent every primary element of each floor including windows, doors, room numbers, architectural decorative elements and so on.
Moreover, A master plan Survey might have several layers of key plans documenting intended changes over time and the scheduled roll out of the changes.
However, A master plan would have separate key plans for each building on the property and each floor of each building
In fact, these are typically used to discuss broad changes and room layout without fussing over assembly details.
What is a Master Plan Survey?
A master plan survey is a planning process conducted to collect, analyse, and evaluate information for the development of a specific area or project. It typically serves as part of a larger master plan, where various aspects of the area, such as geography, population, infrastructure, environmental conditions, and social and economic status, are analysed.
Main Objectives of a Master Plan Survey:
- Data Collection:
Gathering necessary information and data about the area, such as land use, housing density, infrastructure, and environmental features. - Survey Strategy:
Determining appropriate survey methods, such as interviews with local residents, collection of statistical data, and analysis of satellite images. - Analysis:
Analysing the collected data to understand the current conditions of the area and potential future needs. - Recommendations:
Developing planning strategies and policies based on the data to meet the needs of the local community. - Review and Evaluation:
Sharing the survey results with local government to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments to the plan.
Components of a Master Plan Survey:
- Land Use Analysis:
Identifying different land uses, such as residential, commercial, and industrial areas. - Social and Economic Conditions:
Analysing the economic status and social needs of the local population. - Environmental Conditions:
Reviewing the health of the area’s environment and the status of natural resources. - Infrastructure:
Analysing existing infrastructure, such as roads, water supply, electricity, and communication systems.
A master plan survey is an important process that helps ensure effective and sustainable development for local communities.

What is a Site Plan?
Likewise, A site plan is a readable map or residential diagram depicting the plot of land on which a house or building sits. Similarly, along with the landscaping, topography, exterior features, additional service buildings and facilities, etc. included. Additionally, A master plan survey would include a current site plan and as many future site plans as required to document the entire long-term development of the site/land area.
A site plan is a detailed design or outline created for the use of a specific location or site. It is designed according to the geographic, social, and environmental characteristics of the site, providing a precise plan for the site’s intended use, structures, infrastructure, and transportation connections. The primary purpose of a site plan is to ensure the optimal use of the location, fulfilling the needs of the local community while maintaining environmental protection.
Key Components of a Site Plan:
- Land Use: Determining the land use for different parts of the site, such as residential, commercial, industrial, parks, and other amenities.
- Infrastructure Planning: Planning the essential infrastructure of the site, such as roads, water supply, electricity, and drainage systems.
- Transportation Systems: Planning roads for vehicular and pedestrian movement, as well as public transport arrangements and pathways.
- Environmental Considerations: Developing strategies to ensure the conservation of nature and environmental protection, such as managing green spaces and water resources.
- Social Amenities: Planning for educational, health, recreational, and other social services on the site.
- Local Laws and Regulations: Ensuring planning is consistent with local government laws and zoning regulations.
- Project Timeline: Establishing a schedule and phases for development.
Objectives of a Site Plan:
- Integrated Development: Facilitating coordination among various activities based on the site’s potential.
- Visionary Planning: Preparing for future changes and demands.
- Environmental Protection: Ensuring environmental protection for sustainable development.
- Community Benefits: Enhancing amenities and services for citizens.
In summary, a site plan is an essential tool that helps ensure the development and management of a specific location or site, improving the quality of life for local residents.
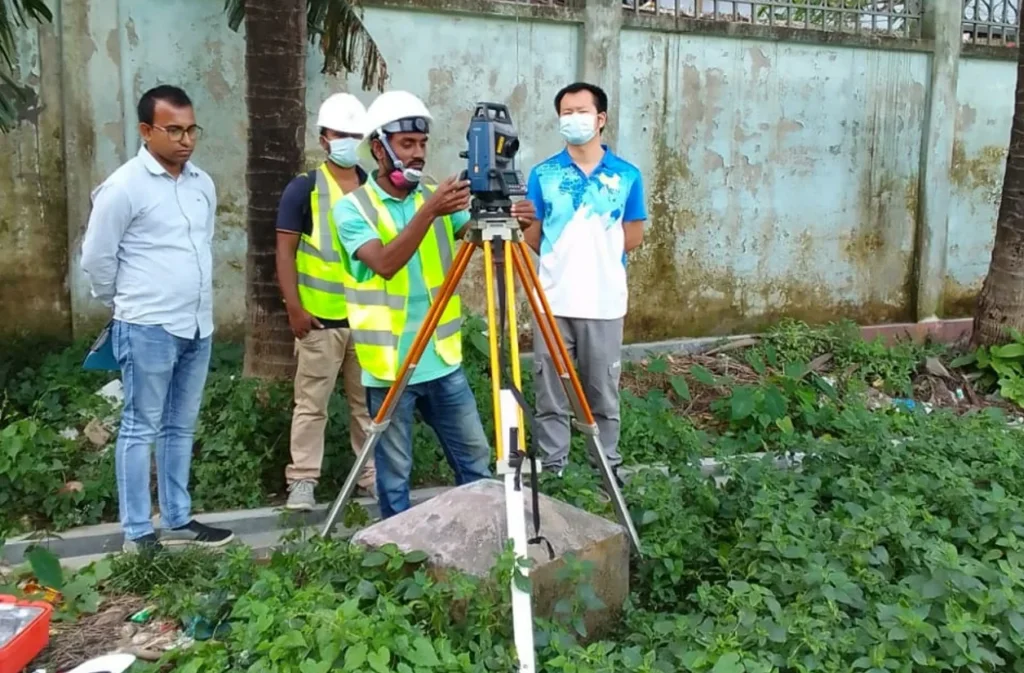
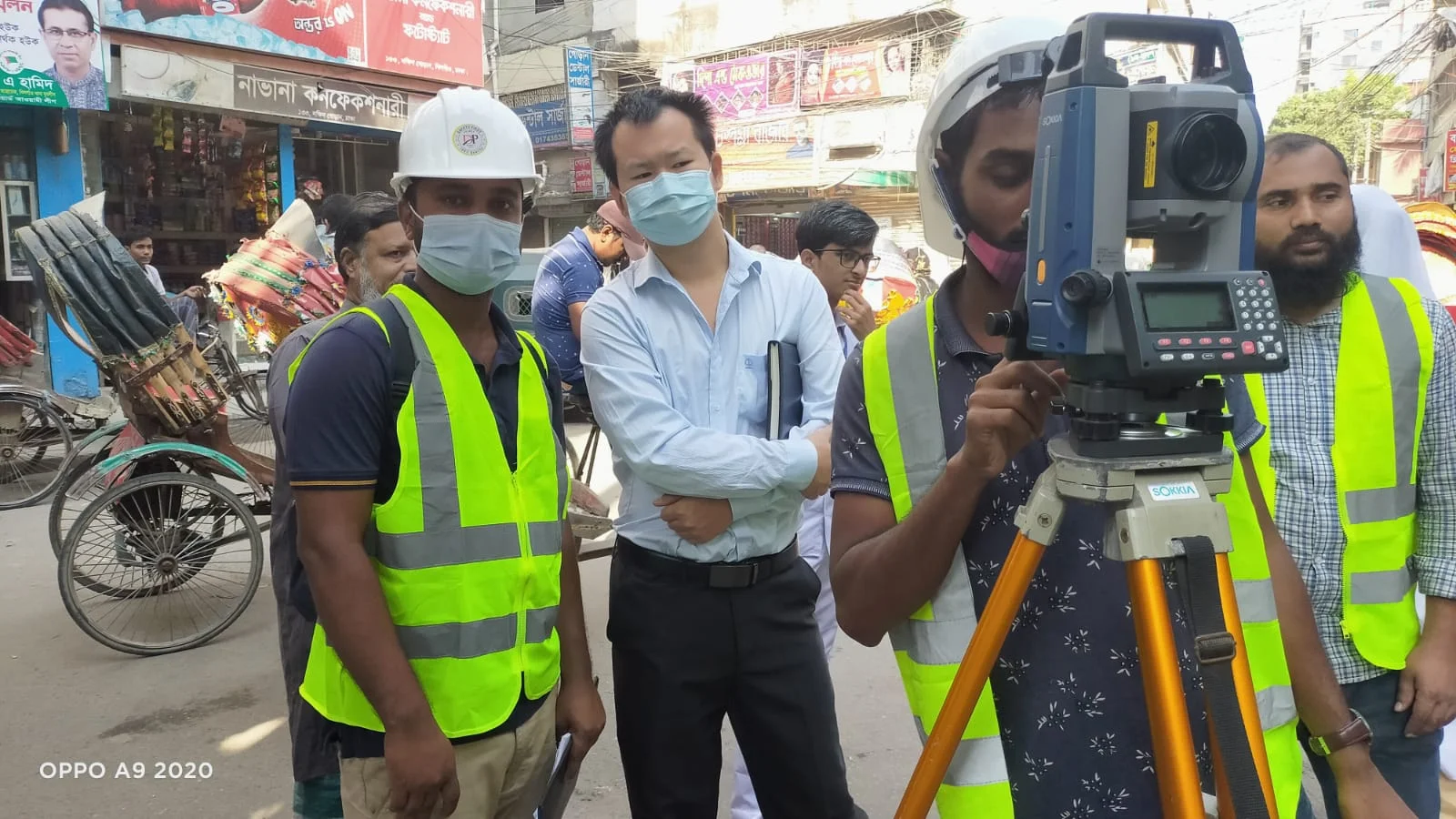
Master Planning using Digital Total Station
Creating a master plan using a digital total station is a highly important and effective method, especially when it comes to accuracy and detailed data collection. When conducting a land survey for a master plan, a digital total station enables precise and real-time data collection, playing a supportive role in project planning and development.
The advantages of creating a master plan using a digital total station are as follows:
- Accuracy and Precision:
- Total stations provide a high level of precision, which is essential for land, structure, and boundary determination. This ensures that each measurement for the master plan is accurate.
- Speed of Data Collection:
- Digital total stations collect data quickly, making survey work faster and more efficient for large projects. They can capture coordinates of multiple points simultaneously.
- Digital Data Integration:
- Data collected from a total station can be directly imported into CAD, GIS, and other design software. This facilitates the creation of digital maps, analysis, and the development of the master plan.
- Reduced Labour Requirements:
- Survey work can be completed with fewer workers, as the digital total station can automatically collect and process data. This reduces costs and saves time.
- Boundary and Terrain Determination:
- Accurate boundary and terrain determination is critical for master planning. The total station can easily define precise boundaries, which is useful for land management and planning.
- Less Sensitivity to Weather:
- Digital total stations can operate in various environmental conditions, maintaining survey accuracy even in adverse weather.
- Land and Structure Analysis:
- Using a total station, information about land and structures can be collected, which is crucial for master planning. It helps in gathering elevation, slope, and other geological data.
Summary:
Creating a master plan using a digital total station is time-saving, accurate, and cost-effective. It is highly beneficial for land management, boundary determination, and structural analysis, playing a critical role in project planning and design development.
Master Planning using RTK GPS
Creating a master plan using RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) GPS technology is a highly effective method that offers advanced accuracy and efficient data collection. When conducting land surveys for a master plan, RTK GPS provides significant benefits, as outlined below:
Advantages of Master Planning using RTK GPS:
- Higher Accuracy:
- RTK GPS technology can achieve positional accuracy within 1-2 centimetres. This is crucial for master planning, where precise boundaries and localised information are essential.
- Rapid Data Collection:
- RTK GPS enables quick and easy determination of multiple points simultaneously, which helps reduce survey time.
- Real-Time Data:
- RTK technology provides real-time, accurate positional data, which helps minimise errors during surveys.
- Automated Processing:
- RTK GPS is designed for automated data processing, aiding in the analysis of land, boundaries, and other structures.
- Easy Data Integration:
- Data collected from RTK GPS can be easily imported into digital maps and CAD/GIS software, simplifying the master planning process.
- Multi-Dimensional Data:
- RTK GPS supports the collection of 3D data, which is helpful for analysing land elevation and other geographic features.
- Internal Structure Accuracy:
- RTK GPS can be used to ensure accuracy in internal construction and structure layout during the master planning phase.
Summary:
Using RTK GPS for master planning is a modern and efficient approach. Its high accuracy, rapid data collection, and real-time data features enhance the precision and effectiveness of the master plan. This technology improves land management and planning processes, contributing significantly to the overall success of the project.