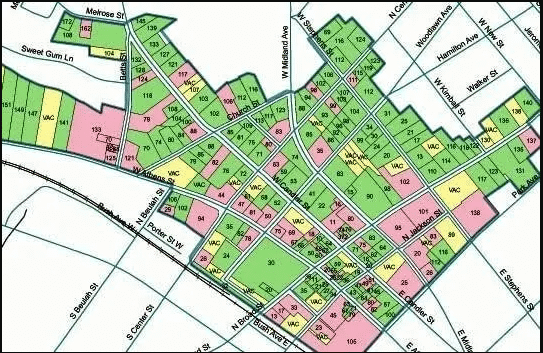
What is a Township Survey?
A township survey is a land surveying method primarily used in the United States. In this method, land is divided into well-planned blocks for surveying, known as “townships.” Each township is typically 6 miles by 6 miles (36 square miles) in size, and it is further subdivided into smaller sections or blocks.
Key Elements of a Township Survey:
- Township: An area divided into 36 sections, with each section being 1 mile by 1 mile.
- Section: One of the 36 parts of a township, with each section covering 640 acres.
- Baseline and Meridian: Township surveys use specific baselines (east-west) and meridians (north-south) for reference.

The Process of Township Survey:
- Climate and Geography: The survey process begins with gathering information about the local climate and geography.
- Boundary Determination: The boundaries of the township are determined, and geological maps are created.
- Guidelines and Maps: Accurate maps of the township and its sections are created, which are then used for future development and land management.
Purpose:
The purpose of a township survey is to ensure proper land use, simplify land ownership and management, and aid in planning for various development projects.
This survey is important for land management, urban planning, and agricultural development.
Introduction of Township Survey
The township survey was originally introduced as a land management system in the United States. It was first implemented in 1785, with the establishment of the Public Land Survey System (PLSS). The primary objective was to accurately survey government land and define boundaries for land sales.
Reasons for the Introduction of Township Survey:
- Land Management and Development: To ensure proper use of land for new settlements and agricultural activities.
- Land Sales: To accurately define boundaries for the sale of government-acquired land.
- Clear Boundaries: To create precise land boundaries to avoid disputes and clarify land ownership.
- Urban Planning: To create accurate maps and plans for the development of urban and rural areas.
The Process of Introduction:
The township survey method was first used to survey newly acquired land in the western regions of the country. In this system, each township was divided into smaller sections, with each section being 1 square mile. This made land easier to sell and manage.
Impact:
This method played a crucial role in land management and urban planning in the United States. Additionally, the township survey method has influenced land surveys in various developing countries, especially where large-scale land management is necessary.
In Summary:
The township survey was introduced as a fundamental method of land management, and it is still used today in land management, urban planning, and agricultural development.
Township Survey Company in BD
Conduct a project survey for the township to prepare maps regarding the following:
- Topography
- Street survey
- Property demarcation
- Water supply
- Sanitary system
- Electrification system
- Telephone system
Moreover, we will describe the procedure for preparing these maps later. However, the development authority of the city or town conducts all the surveys. In fact, Cooperation with concerned departments like the Roads Department, Municipality or Corporation, Electric Supply Department, Telephone Department, etc.
Indeed, the Public Land Survey System (PLSS), we generally refer to township survey by a number. A Citation to the township will look something like this. Likewise, we use Markings like ‘Township 2 North Range 3 East’ or ‘T2N, R3E’ in property descriptions based on the PLSS.”
The United States General Land Office Initially surveyed and platted Township Surveys. They used Employed private survey crews to mark these surveys on the United States Geological Survey maps of the United States.

Township Survey Details
Township Survey is a land surveying method primarily used for the management, sale, and development of land. It is most commonly associated with the United States, where it has been a key system for organising land into well-defined sections. The township survey is part of the Public Land Survey System (PLSS), and it plays a vital role in land planning and management.
Key Features of Township Survey:
- Size of a Township: A typical township is 6 miles by 6 miles, covering an area of 36 square miles. Each township is subdivided into sections, with each section being 1 square mile or 640 acres in size.
- Sections and Subdivisions: Each section can be further divided into smaller parts, which can be allocated for various purposes like agriculture, settlement, or industrial development.
- Baseline and Meridian: In the township survey, specific baselines (east-west) and meridians (north-south) are used as reference points for dividing and measuring land. These lines provide a guide for accurate boundary marking and map creation.
Importance of Township Survey:
- Land Management: Township surveys ensure that land boundaries and measurements are accurate, which is essential for land sales and management purposes.
- Urban and Rural Planning: By providing precise plans, township surveys aid in the development of new settlements, agricultural areas, and infrastructure such as roads and communication networks.
- Clarification of Land Ownership: Accurate surveying and division of land help avoid disputes and ensure clear ownership rights, which is essential for legal land transactions.
- Development and Expansion Plans: Townships serve as a framework for the orderly expansion of cities and rural areas, helping in the long-term development of land resources.
Application:
Township surveys are typically used for large-scale land areas where proper planning and management are necessary. They are effective in areas designated for agricultural, residential, and industrial purposes, providing a systematic approach to land development.
Summary:
The township survey is a structured and precise method for land management, ownership determination, and development planning. It is an essential tool for organising land into manageable units and has been crucial in the growth of cities, agricultural lands, and infrastructure projects in the U.S. and other regions where large-scale land management is required.
About Township Survey
Moreover, this kind of township survey is similar to geographic townships in the province of Ontario, Canada.
Indeed Kentucky, they divide the Jackson Purchase area (west of the Tennessee River) into townships and ranges.
In Tennessee, they survey the entire state into townships and ranges, which together form 13 survey districts managed by the Tennessee State Survey. Indeed, the far northern region of Maine, they divide an area into townships and ranges oriented to true north.
In the central part of the state, they divide a region comprising 17 surveys into townships. Yet, these townships do not align with true north. The remainder of the state is on metes and bounds. vermont and New Hampshire, which are primarily metes-and-bounds states, also feature regions in the north that have townships surveyed without orientation to true north.
The majority of Ohio is surveyed using the Public Land Survey System. But also, there are several substantial areas that follow metes-and-bounds, including the Virginia Military Reserve, Donation Tract, French Grant, and the three Moravian grants (Gnadenhutten, Schoenborn, and Salem).
Clark’s Grant, a 150,000-acre (61,000 ha) area in southern Indiana, is not divided into townships but is still subject to a gridded survey. Similarly, Portions of the Texas State Survey use square township survey.
Moreover, Sizeable portions of Alaska, Arizona, California, Idaho, Montana, Oregon, and Washington, are unsurvey. Substantial swampy areas in Florida and Louisiana are also surveyed.

Need for Township Survey
The need for a township survey is crucial for land management, planning, and development. It helps in the accurate division of land, determining ownership, and providing necessary data for future development activities. Township surveys are mainly used for large land areas where regular planning and management are essential.
Necessity of Township Survey:
- Accurate Division of Land: Township surveys divide land into specific portions, which is crucial for proper land utilisation. It helps in determining suitable land for new settlements, agricultural development, and industrial areas.
- Determination of Ownership: By conducting accurate surveys, the boundaries of the land are defined, which helps in confirming land ownership. Township surveys ensure ownership based on accurate measurements and documentation, helping to avoid legal disputes.
- Development Planning: For the planning of new urban or rural areas, township surveys are essential in properly organising roads, water, electricity, and other facilities. It serves as a foundation for architectural planning required for development.
- Avoiding Disputes and Complexities: Township surveys help define land boundaries and layouts, which aids in avoiding land disputes and legal complexities. Proper boundary marking simplifies land transactions and management.
- Agricultural and Industrial Development: Township surveys assist in selecting land for agriculture and industry, identifying fertile land or areas suitable for industrial development. It plays a role in long-term development planning.
In Summary, the Need for a Township Survey:
- Ensuring proper land utilisation.
- Defining land boundaries and ownership.
- Planned development and urban expansion.
- Reducing land disputes and legal complexities.
- Supporting agricultural, industrial, and infrastructure development.
In conclusion, township surveys are essential for land management and planning. They provide critical information for the proper management of land, development, and future expansion, contributing to the country’s long-term economic and social development.
Necessary Equipment for Conducting City Surveys
The following equipment is required to conduct a city survey.
The necessary equipment for conducting a city survey consists of various tools and instruments that help surveyors accurately collect data and determine the boundaries, roads, buildings, and other infrastructures of a city. In city surveys, accuracy and precision are extremely important; therefore, advanced and reliable tools are needed.
Necessary Equipment for Conducting City Surveys:
- Total Station: This is an advanced electronic device used for measuring angles and distances. It allows for the accurate marking of points and their transfer to maps.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS is used in city surveys to pinpoint specific locations on the land and to determine global coordinates. It is essential for fast and accurate location identification.
- Levelling Instrument: This is used to identify land elevation and local changes. It helps determine the correct heights for roads, drains, and other infrastructures.
- Prisms and Reflectors: These are used with a total station to collect reflected laser beams from distant points, making distance measurement easier.
- Field Book and Pencil: A field book is crucial for recording data during the survey. All directions, distances, and other measurement information are documented here.
- Measuring Tape or Chain: Measuring tape or chain is used for measuring short distances. It aids in land division and determining distances between points.
- Drones (UAV): Currently, drones are used for advanced city surveys. They allow for the rapid and accurate creation of maps from elevated viewpoints and can collect satellite views with drone cameras.
- Compass: Used for determining direction. Although modern equipment has simplified this task significantly, a compass still makes it easier to establish precise directions during surveys.
- AutoCAD or GIS Software: After collecting field data, maps are created using AutoCAD or Geographic Information System (GIS) software. This assists architects and engineers in accurate planning.
- Plumb Bob: This is a simple tool used to accurately mark vertical straight lines. It helps determine the heights of land and other structures.
Conclusion:
All of this equipment and tools are crucial for conducting city surveys. They enable the collection and analysis of accurate data, facilitating planned and advanced urban management.
Topographic Map
The entire area is divided into a number of sectors, each of which is enclosed by a polygon. The polygons are connected by common sides. They are treated as closed traverse and the traversing is done by total station.
The interior details are located by plane table or the transit-and tape-method. These details include houses, roads, lakes, parks, railway lines, stations, etc.
Fly levelling is undertaken to establish the RLs of important points and benchmarks. Contouring is done by plane table or tacheometer. The nature of the ground surface is indicated in relief (i.e. colouring, shading, hatching, etc.) on the map.
Finally, all the sectors are assembled in one map so that the township survey area or city area.
Road Map Development
Road map development is an important process used for planning and analysing the road network and infrastructure of an area. The process of creating a road map is divided into various stages, including preliminary data collection, design, and map preparation.
Steps in Road Map Development:
- Data Collection:
- Local Survey: Information about the roads, streets, and other infrastructure of the area needs to be collected.
- GPS Technology: Identifying exact locations using GPS devices.
- Satellite Imagery: Obtaining detailed images of the area through satellite imagery.
- Classification and Planning:
- Road Classification: Roads are categorised into different classes (such as highways, regional roads, local roads).
- Design: Creating the design and planning for the roads, which includes road width, curves, signals, and other facilities.
- Map Creation:
- Digital Software: Using AutoCAD, ArcGIS, or other digital mapping software to create the maps.
- Map Information: Including accurate information on the road map, such as road names, classifications, number of lanes, and other relevant data.
- Review and Revision:
- Feedback: Collecting feedback from local government, planners, and road users.
- Revisions: Making necessary adjustments to the map based on the feedback received.
- Publication:
- Publication: Releasing the created map and making it available to the public.
- Updates: Periodically updating the map to include changes.
Purpose:
The purpose of road map development is to:
- Ensure accurate planning of the road network.
- Reduce traffic congestion and road accidents.
- Assist in the development of local communities.
- Improve mobility and connectivity of vehicles.
The accurate development of road maps is an essential component in the progress of cities, leading to improvements in the lives of citizens.

Preparations of Property Map
This map is also prepared using a large scale to show the boundaries of public and private properties, plot numbers, premises numbers, and so on. The property map is also prepared by plane table by dividing the total township area into different
Water Supply and Sanitary Map
They bury the network of the water supply distribution system and sewer lines underground. To aid in pinpointing specific locations from above. They depict the complete networks of the water supply and sanitary works using conventional lines on the street survey map.
They use specific symbols to mark all essential lines and points, including intake points, purification points, check valves, fire hydrants, manholes, lamp holes, inspection chambers, and more.
Electrification Map: –
Normally, they bury the network of cables for electrification in the township or city underground. Thus, the street survey map should depict the distribution methods using a unique colour scheme or suitable symbols.
They should clearly mark the specific points of the supply line to facilitate easy location in case of a cable fault. The street survey should include the map of the supply system, regardless of the electrification method.
Preparations of Telephone Map: –
The network of telephone cables also lies under the ground. To simplify fault location, the street survey map represents the network system using specific colour conventions or suitable symbols.
Coordination Work for Township Survey
Coordination work for a township survey is an important phase of land surveying that is essential for the proper division and management of land. Through this work, the boundaries, sections, and other important elements of the township are accurately determined. The main steps involved in the coordination work for a township survey are as follows:
Steps in Coordination Work for Township Survey:
- Boundary Determination:
- Local land boundaries and previous survey information are used to determine the boundaries of the township.
- Various processes, such as using reference points or permanent markers, are employed to identify the boundaries.
- Section Identification:
- Each township is divided into 36 sections, with each section measuring 1 mile by 1 mile.
- Equipment and technology are used for the accurate identification of the sections.
- Data Collection:
- Information related to the characteristics and use of the land is collected during the survey.
- Interviews with local people or the use of local documents help gather information about past land use.
- Map Preparation:
- Accurate maps of the township and its sections are created, which are used for future development and land management.
- The map highlights land boundaries, sections, and important locations.
- Review and Revision:
- The results of the survey are reviewed and revised if necessary.
- Feedback is collected from local government or land management authorities.
- Report Preparation:
- A report is prepared that compiles the results of the survey and the map information.
- The report is submitted to the relevant authorities.
Conclusion:
Coordination work for a township survey is essential for the proper use and planning of land. It provides accurate guidance on land ownership, use, and development activities.
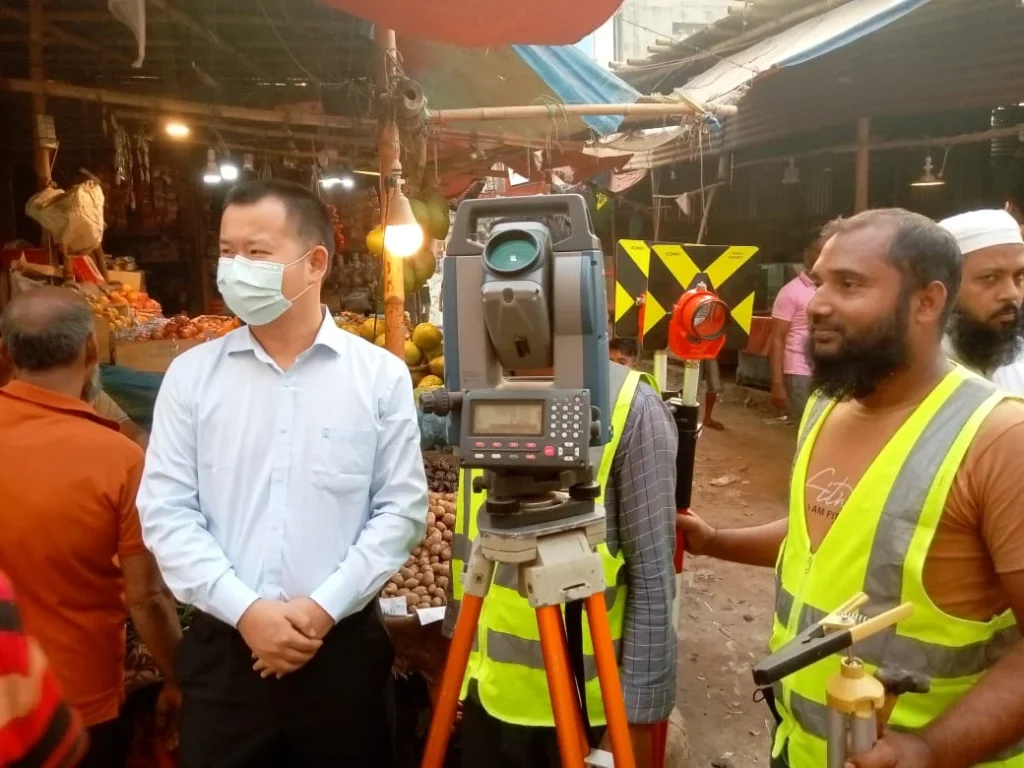
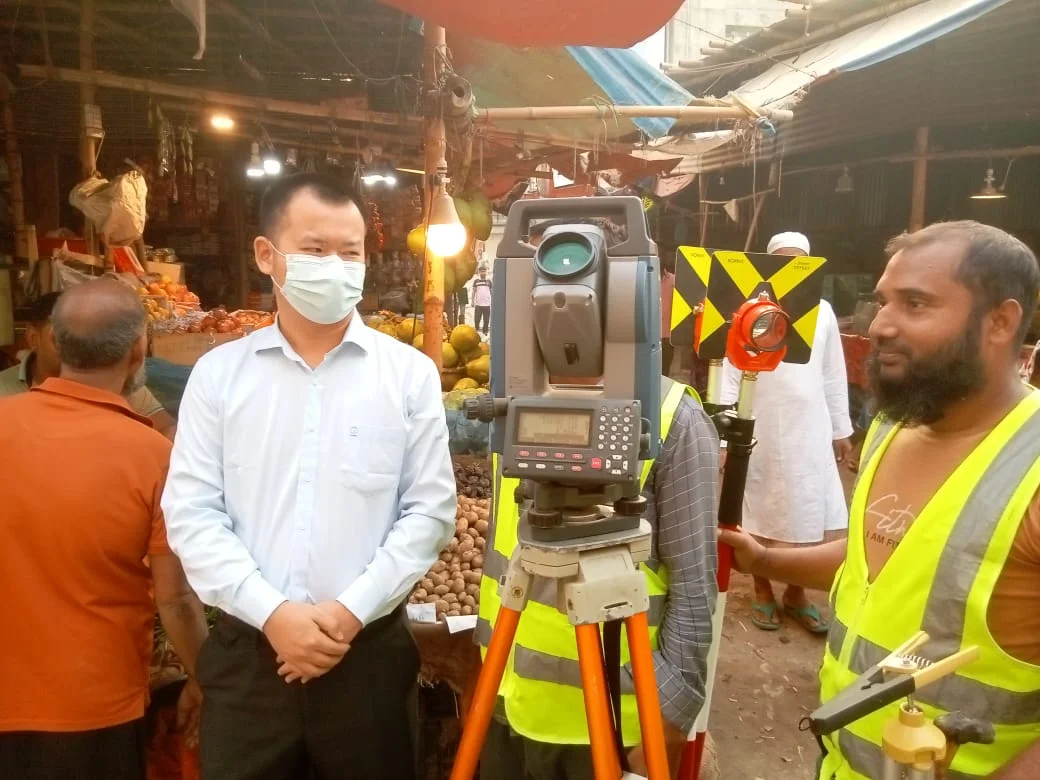
Township Survey using Total Station
The main advantages of conducting a township survey with a Total Station are accuracy, efficiency, and digital data collection capabilities. This modern instrument is especially effective for surveying large areas, like townships, while maintaining precision and efficiency. The benefits of using a Total Station for township surveys are as follows:
- High Accuracy:
- The Total Station provides extremely accurate distance and angle measurements, ideal for township surveys. It allows for precise determination of each point’s position and elevation within the township area.
- Digital Data Collection:
- The Total Station directly records digital data, which can be imported into a computer. This is suitable for creating digital maps and convenient for future analysis.
- Fast Data Processing:
- Surveying tasks can be completed quickly using the Total Station. It measures angles, distances, and elevations simultaneously, saving time.
- Automated Processing:
- The Total Station automatically captures data points, reducing manual errors and enhancing survey accuracy. As a result, large areas can be surveyed efficiently in a short time.
- Topographic Data Collection:
- The Total Station is highly effective for collecting and mapping topographic data in township areas. It helps determine terrain features, such as slopes and elevations.
- Reduced Costs and Labor Requirements:
- The Total Station can conduct surveys with fewer personnel, reducing costs and labour. It is beneficial for efficiently handling large projects like townships.
- Easy Data Integration:
- Data collected from the Total Station can be easily imported into GIS and CAD software, simplifying the planning and design processes.
- Boundary and Land Management:
- Data collected by the Total Station is very useful for determining land boundaries and managing land within a township, aiding in accurate boundary identification.
Summary:
Using a Total Station, township surveys can be conducted effectively and accurately. It aids in land use, boundary determination, and topographic data collection, providing reliable information while reducing time, costs, and labour requirements for large projects.
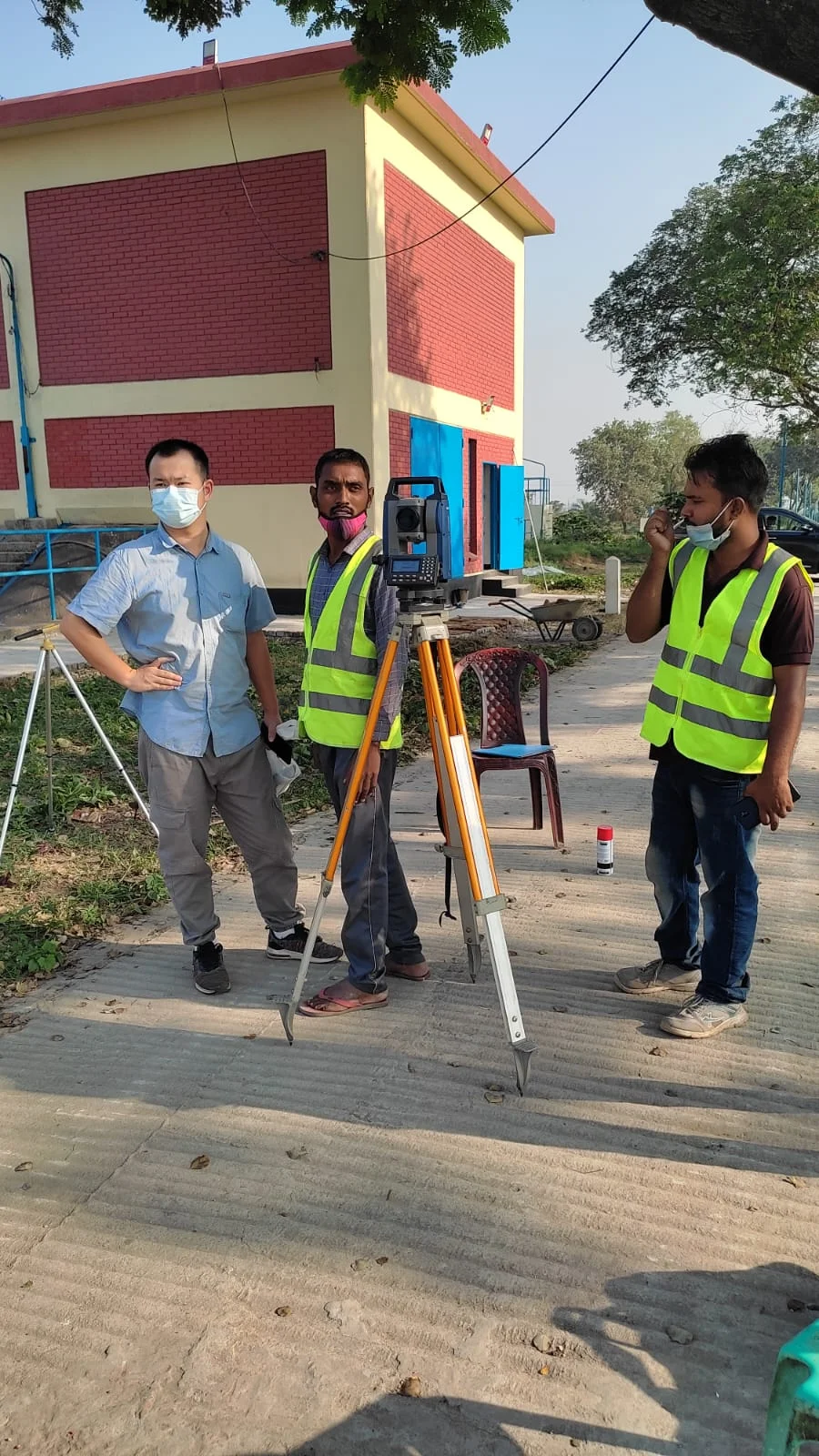
Township Survey using RTK GPS
Conducting a township survey using RTK GPS (Real-Time Kinematic GPS) is highly effective as it facilitates high precision and rapid terrain measurement. RTK GPS improves the township survey process and plays a significant role in saving time and costs.
The benefits of using RTK GPS for township surveys include:
- High Accuracy:
- RTK GPS offers centimetre-level accuracy, which is crucial for township surveys. It helps determine the precise coordinates of each land point.
- Rapid Data Collection:
- RTK GPS provides real-time data, helping to complete survey tasks quickly. It can simultaneously collect coordinates of multiple points, making the township survey more efficient.
- Wide Area Coverage:
- RTK GPS can survey large areas, making it ideal for surveying extensive regions like townships.
- Automated Data Processing:
- RTK GPS directly collects digital data, which is very convenient for data management and analysis. The data can be easily imported into GIS and CAD software.
- Quick Adjustments and Updates:
- Necessary updates can be quickly identified and integrated during the township survey. RTK GPS can adapt rapidly to the local environment through multiple base stations.
- Reduced Labour Needs:
- RTK GPS requires less manpower, as it can automatically collect data. This reduces costs and minimises labour requirements.
- Boundary and Land Management:
- RTK GPS aids in accurately determining land boundaries, which is crucial for land management and development projects within townships.
- Less Sensitivity to Weather:
- RTK GPS technology can operate in various environmental conditions, maintaining accuracy even in poor weather.
Summary:
Using RTK GPS for township surveys enables high accuracy and speed, supporting land management, boundary determination, and other survey activities. It saves more time and labour compared to traditional methods, while also providing enhanced data analysis and digital mapping capabilities.