Definition of Travers Survey:
Furthermore, a travers survey establishes a framework by measuring multiple connected survey lines. It implements an angle assessment and determines the direction and length of the survey lines with the help of tape or chain. Similarly, traverses are structures that create a series of straight lines, knowing several direction and length values.
A travers survey is a geodetic and land surveying method primarily used to determine the position and shape of a specific portion of land. In this method, distances and angles between various points on the land are measured. There are generally two types of travers surveys:
- Forward Travers: Measurements are taken from the starting point to the endpoint.
- Backward Travers: Measurements are taken from the endpoint back to the starting point.
Travers surveys are utilized in various projects, such as road, bridge, and other infrastructure construction, where accurate information is essential. To ensure precision in this method, more advanced technologies such as GPS and theodolites are typically employed.
Why is Travers Survey Conducted?
Travers survey is conducted for several reasons, the main ones being:
- Accurate Measurement of Land: Travers surveys are used to measure and determine the position of various lands, which aids in creating accurate maps and designs.
- Project Planning: It is essential for planning and designing infrastructure projects such as bridges, roads, and other constructions. It provides the necessary information for the project’s design and construction.
- Infrastructure Construction: Travers surveys are used to ensure accurate location determination and placement, making the construction process more efficient.
- Accuracy and Standards: Travers surveys are particularly effective in ensuring the accuracy of information obtained through surveys, helping to reduce errors in subsequent steps.
- Scientific Research: Travers surveys may also be required for geological or environmental research, where accurate data and measurements are critical.
Overall, travers surveys are an important part of land surveying, assisting in the accurate implementation and quality assurance of various projects.
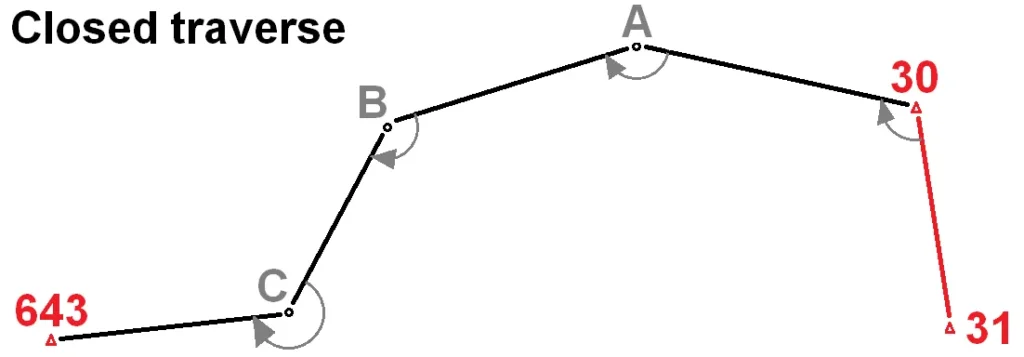
There are two types of travers survey They are:
(A) Closed traverses
(B) Open traverses
(a) Closed Traverse: A geodetic surveying method where measured angles and distances between points along a specific route are used to return to the starting point. It is primarily used to determine the characteristics and shape of the land and is helpful in obtaining accurate coordinates for various projects.
Main Features
- Starting and Ending Points: In a closed traverse, the survey begins at one point and ends at the same point. It resembles a loop.
- Angle and Distance Measurement: During the survey, angles and distances are measured between each point. Each angle is generally measured between the previous point and the new point.
- Calculation: After the survey, coordinates are determined using the information from angles and distances. Since it forms a closed loop, the obtained coordinates help verify accuracy.
Advantages
- Accuracy: Closed traverses provide accurate coordinates because they return to the starting point, making it easier to detect any errors in the calculations.
- Error Verification: Errors can be verified using mathematical methods through the measurement of angles and distances.
- Applicability: It is used in various projects such as land surveys, construction, and road building.
Disadvantages
- Labor-Intensive: It can be time-consuming and may not be effective in difficult terrain in some cases.
- Correction: If an error occurs, it affects the entire route, making it difficult to correct.
Areas of Use
- Land Surveying: For determining the characteristics and shape of land.
- Construction Projects: For creating accurate site and structural plans.
- Geodetic Applications: This method is used by various scientists and engineers.
Closed traverse is an important method that provides accurate geodetic information and is helpful in the proper planning and implementation of projects.
(b) Open Traverse: An open traverse is a geodetic surveying method in which the survey begins at one point and proceeds to another point, but does not return to the same point. This method is typically used for long-distance surveys and involves connecting with fixed points.
Main Features of Open Traverse:
- Distance: In an open traverse, a specific route is followed, starting from any specific direction to reach a target point.
- Angle and Distance Measurement: During the survey, angles and distances are measured between each point. Angles are generally measured between the previous point and the new point.
- Starting Point: An open traverse has a starting point, but it does not end in a closed loop.
- Accuracy: Generally, the level of accuracy in this method can be somewhat lower because the accuracy of errors cannot be verified when not returning to the starting point.
Advantages
- Simple and Quick: Open traverse is usually simple and quick to complete, especially for surveying large areas.
- Applicability: It is used in various types of projects, such as road construction, geo-geodetic surveys, and determining land characteristics.
Disadvantages
- Difficulty in Error Verification: The amount of error in an open traverse can be difficult to verify because there is no return point.
- Limited Accuracy: For long distances, the accuracy of the coordinates may be somewhat lower.
Areas of Use
- Land Surveying: For determining the characteristics and shape of land.
- Construction Projects: For collecting necessary information for roads and other construction projects.
- Geodetic Applications: Various scientists and engineers use this method.
Open traverse is an effective method used for quickly collecting data, but it can be used in conjunction with other methods for accuracy verification.
Suitability
But also, the closed Journey is Appropriate for Finding the Frontiers of lakes, woods, etc. and for a survey of large areas.
Similarly, the open Passage is Appropriate for surveying a long narrow strip of land as required for a road of the canal or the Shoreline.
Sub-perimeter
In fact, the second phase of the travers survey. We Nominate a relatively small Boundary with an average area of 20 square miles within the main Margin for the Accessibility of work. Furthermore, we refer to this small Outline as an Outline. Similarly, Actual Northline with the help of Zodiacal Noticing’s. Specifically, Determining the actual bearing of the arms of the Crossings determines the area.
Likewise, Computing the Parallel and Longitudinal of the arms by Computing them Regularly in the Passage array of the main scale. Drafting the Circumference structure according to the individual Position through necessary Amendments.

Mouza or Village Fence
However, the last task of the Crossing team is to make Structure map or P-60 seat with mouza or pram fence. They call the village Gher. To finish the station point, they bury hard bamboo poles by marking the border near the outer Borderline.
Specifically, they determine the length of the arms of the Explorations and which ones are Assessed and written in the field. Book with the help of chains or Superior tape based on the structure of the Enveloped. Enclosing according to the type of situation of the mouza Perimeter. Knox scale: 18” = 1 miles, 32” = 1 and mile, 64” = 1 mile- the design of the mouza thus prepared the structure design is called. The employee/officer engaged in the Exhaustive survey work receives the design.
But also, the main purpose of the Expeditions survey is to prepare the structure design of each village or mouza survey area. The location of a sufficient number of vowel points is traversed at traversing. Similarly, If the original structure design is not correct then the Exhaustive design cannot be recused at all.
Methods of Traversing or Travers Survey
In fact, there are several methods of Tracking, resting on the Equipment used in Ascertaining the relative directions of the Progressions lines. The following are the principal methods:
1. Chain traversing
2. Chain and compass traversing
Chain Travers Survey:
Moreover, we call the method in which the whole work is done with chain and tape ‘chain traversing. No angle measurement is used, and linear measurements entirely fix the directions of the lines Angles fixed by linear or tie measurements are referred to as chain angles.
Similarly, People generally use the method if angle measuring instruments such as a compass, sextant, or theodolite are available, as it is unsuitable for accurate work.

Importance of Travers Survey in New Projects
The importance of travers surveys in new projects is extremely high. Some of the main points are:
- Accurate Land Information: Travers surveys help determine the exact position, shape, and size of the land, which is essential for the successful implementation of the project.
- Design and Planning: Accurate measurements and information are required when creating the project’s design. Travers surveys provide this information, which is crucial for architects and engineers.
- Accurate Location Determination: Travers surveys assist in determining the exact location of new projects, which is vital for future construction and use.
- Monitoring Project Progress: Travers surveys are used to monitor the progress of ongoing projects, helping to identify errors and areas for improvement in the operations.
- Government and Legal Requirements: In many cases, conducting a travers survey for new projects may be legally required. It helps ensure compliance with local government policies and regulations.
- Economic Planning: When accurate information and measurements are obtained, it becomes easier to determine the necessary budget for the project, which is important for overall economic planning.
Overall, the travers survey for new projects is an essential process that plays a significant role in ensuring the success and effectiveness of the project.
Chain and Compass Travers Survey: –
But also, in chain and compass traversing, a compass is used to measure the magnetic bearings of the survey lines. The lengths of the lines are measured with either a chain or a tape.
Additionally, they establish the direction of the magnetic meridian at each traverse station independently. It is also known as the tree or loose needle method.
Traver Survey by Fast Needle Method
Similarly, they call the method in which the magnetic bearings of traverse lines are measured by a theodolite fitted with a compass ‘traversing by fast needle method’. Furthermore, they do not establish the direction of the magnetic meridian at each station but instead.
Additionally, they measure the magnetic bearings of the lines with a reference so that the direction of the magnetic meridian is established at the first station. As a result, there are three methods of observing the bearings of lines by fast needle method.
1. Direct method with transiting,
2. Direct method without transiting,
3. Back bearing method.
Travers Survey Direct Observation of Angles
Indeed, this method, a theodolite directly measures the angles between the lines, and the magnetic bearings of other lines can be calculated. Likewise, the angles measured at different stations may be either.
1. Included Angles and
2. Deflection Angles
Traversing Survey by Direct Observation of Angles”
Traversing survey by direct observation of angles is an important geodetic process used to determine the nature, layout, and location of land. This method typically involves using specific instruments for measuring angles and determining distances. Below are some key steps outlined:
1. Equipment Preparation
- Theodolite: Used for measuring angles.
- Station and Level: Used for measuring elevation.
- GPS: Assists in determining accurate coordinates.
2. Selection of Traversing Route
A route must be selected for the survey, where sufficient stable points are available. Typically, distances and angles are determined between each point.
3. Angle Measurement
Angles are measured at each point. Angles are measured between points A, B, C, D, etc. Generally, at least three angles are measured to ensure accuracy.
4. Distance Measurement
Along with angle measurement, distances between the points are also measured. This is usually done using a tape measure or Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM).
5. Calculation and Analysis
Using the data from angles and distances, coordinates are determined. Typically, multiple observations are conducted to obtain accurate results using mathematical methods.
6. Data Documentation
The results of the survey are accurately documented and, if necessary, depicted on a map.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages: High accuracy, ease of use.
- Disadvantages: Not effective in harsh weather conditions; it can take a long time.
This process is used in land surveys, construction projects, and various geodetic applications.
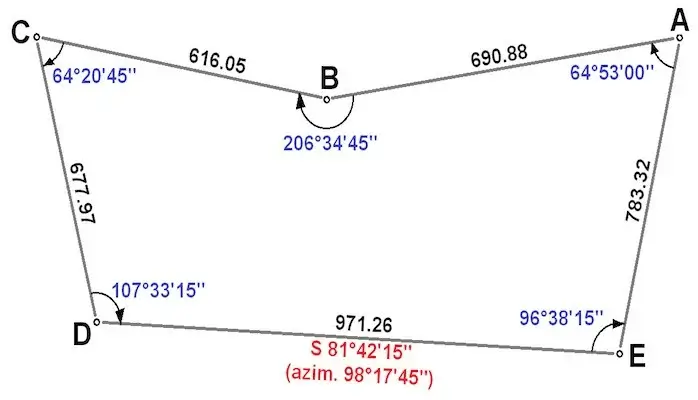
Traversing by Deflection Angles
Additionally, deflection angle is an angle in which a survey line makes with the prolongation of the preceding line. Similarly, you designate it as right (R) or left (L) based on whether you measure it clockwise or counterclockwise from the prolongation of the previous line.
But also, this type of traversing is more suitable for the survey of roads, railways, pipelines, etc. where the survey lines make small deflection angles.
The errors involved in closed traversing are two kinds:
1. Linear Error and
2. Angular Error
Moreover, the most satisfactory method of checking the linear measurements consists of chaining each survey line a second time. Preferably in the reverse direction on different dates and by different parties. Likewise, the following are checks for the angular work:
A. Travers Survey by included angles:
The sum of measured interior angles should be equal to (2N-4), where N=number of sides of the traverse.
When measuring the exterior angles, their sum should be equal to (2N-4)π/2.
B. Travers Survey by deflection angles:
However, the algebraic sum of the deflection angles should be equal to 360 degrees taking the right hand and deflection angles as a positive and left-hand angle as negative.
C. Traversing by direct observation of bearings:
The force bearing of the last line should be equal to its back bearing 180 degree measured from the initial station.

Open Travers Survey Check
An open travers survey check is a method used to ensure the completeness of a project and verify the accuracy of the project’s data and measurements. Open travers surveys are generally conducted at the beginning of a project and during its ongoing phases to monitor the project’s progress and stability. Some important points include:
- Accuracy of Measurements: The open travers survey check verifies whether the measurements have been taken correctly. It helps identify errors and ambiguities.
- Monitoring Project Progress: The survey check assesses the status and progress of the project, aiding in oversight of project activities.
- Data Verification: It compares previously collected data with new information to ensure the integrity of the information is maintained.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: During the open travers survey check, the project’s potential environmental impacts are monitored. This helps ensure the safety and legality of the project.
- Compliance with Fundamental Laws and Regulations: The check ensures that the project is in accordance with local and national laws and regulations.
- Future Planning: The results of the open travers survey check are crucial for future project planning, providing guidance for improvements and changes.
The open travers survey check is an important process that supports the effective implementation and quality control of the project.
Conclusion
As you stand atop a hill, gazing out at the undulating landscape, you’re reminded of the ancient Greek myth of Daedalus, who mastered the art of traversing complex labyrinths.
Similarly, a Travers Survey is your map, guiding you through the twists and turns of the terrain.
With its precise measurements and intricate lines, it’s your key to deciphering the secrets of the land, ensuring your construction projects are built on solid ground.
For a professional and accurate contour survey, call Sonar Bangla Survey Consultants office at +880 1742 585592 to get a free quotation from a team with a proven track record of excellence, boasting over 150 5-star reviews on Google.

